Page 215 - Fundamentals of Computational Geoscience Numerical Methods and Algorithms
P. 215
206 8 Spontaneous Crack Generation Problems in Large-Scale Geological Systems
5.00E+07
CS = 10MPa
CS = 1MPa
4.00E+07 CS = 0.1MPa
Deviatoric Stress (Pa) 3.00E+07
2.00E+07
1.00E+07
0.00E+00
0.00 0.04 0.08 0.12
Axial Strain
(A) 1× m sample
2
5.00E+07
CS = 10MPa
CS = 1MPa
4.00E+07
CS = 0.1MPa
Deviatoric Stress (Pa) 3.00E+07
2.00E+07
1.00E+07
0.00E+00
0.00 0.04 0.08 0.12
Axial Strain
2
(B) 1× km sample
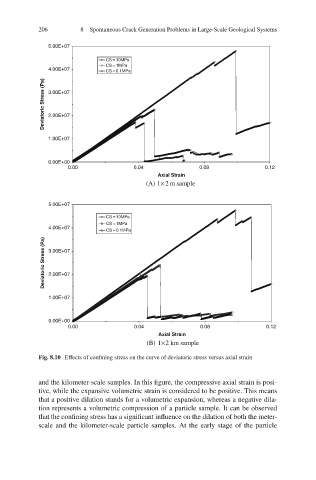
Fig. 8.10 Effects of confining stress on the curve of deviatoric stress versus axial strain
and the kilometer-scale samples. In this figure, the compressive axial strain is posi-
tive, while the expansive volumetric strain is considered to be positive. This means
that a positive dilation stands for a volumetric expansion, whereas a negative dila-
tion represents a volumetric compression of a particle sample. It can be observed
that the confining stress has a significant influence on the dilation of both the meter-
scale and the kilometer-scale particle samples. At the early stage of the particle