Page 208 - Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery
P. 208
196 Mohammad Ali Ahmadi
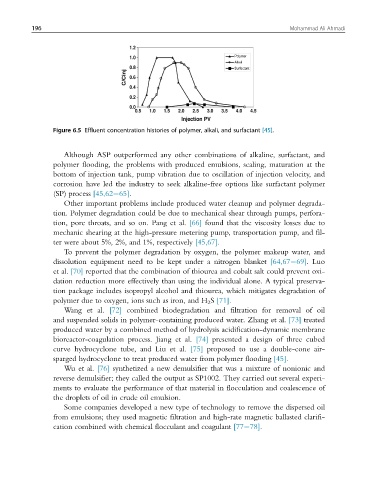
Figure 6.5 Effluent concentration histories of polymer, alkali, and surfactant [45].
Although ASP outperformed any other combinations of alkaline, surfactant, and
polymer flooding, the problems with produced emulsions, scaling, maturation at the
bottom of injection tank, pump vibration due to oscillation of injection velocity, and
corrosion have led the industry to seek alkaline-free options like surfactant polymer
(SP) process [45,62 65].
Other important problems include produced water cleanup and polymer degrada-
tion. Polymer degradation could be due to mechanical shear through pumps, perfora-
tion, pore throats, and so on. Pang et al. [66] found that the viscosity losses due to
mechanic shearing at the high-pressure metering pump, transportation pump, and fil-
ter were about 5%, 2%, and 1%, respectively [45,67].
To prevent the polymer degradation by oxygen, the polymer makeup water, and
dissolution equipment need to be kept under a nitrogen blanket [64,67 69]. Luo
et al. [70] reported that the combination of thiourea and cobalt salt could prevent oxi-
dation reduction more effectively than using the individual alone. A typical preserva-
tion package includes isopropyl alcohol and thiourea, which mitigates degradation of
polymer due to oxygen, ions such as iron, and H 2 S [71].
Wang et al. [72] combined biodegradation and filtration for removal of oil
and suspended solids in polymer-containing produced water. Zhang et al. [73] treated
produced water by a combined method of hydrolysis acidification-dynamic membrane
bioreactor-coagulation process. Jiang et al. [74] presented a design of three cubed
curve hydrocyclone tube, and Liu et al. [75] proposed to use a double-cone air-
sparged hydrocyclone to treat produced water from polymer flooding [45].
Wu et al. [76] synthetized a new demulsifier that was a mixture of nonionic and
reverse demulsifier; they called the output as SP1002. They carried out several experi-
ments to evaluate the performance of that material in flocculation and coalescence of
the droplets of oil in crude oil emulsion.
Some companies developed a new type of technology to remove the dispersed oil
from emulsions; they used magnetic filtration and high-rate magnetic ballasted clarifi-
cation combined with chemical flocculant and coagulant [77 78].