Page 210 - Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery
P. 210
198 Mohammad Ali Ahmadi
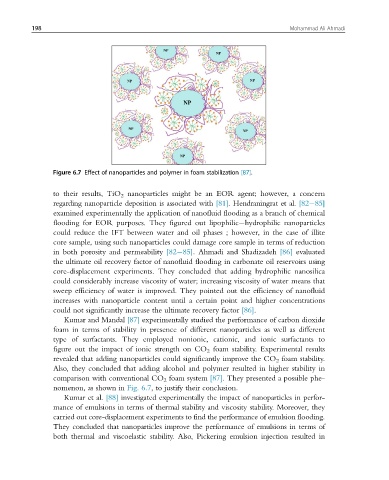
Figure 6.7 Effect of nanoparticles and polymer in foam stabilization [87].
to their results, TiO 2 nanoparticles might be an EOR agent; however, a concern
regarding nanoparticle deposition is associated with [81]. Hendraningrat et al. [82 85]
examined experimentally the application of nanofluid flooding as a branch of chemical
flooding for EOR purposes. They figured out lipophilic hydrophilic nanoparticles
could reduce the IFT between water and oil phases ; however, in the case of illite
core sample, using such nanoparticles could damage core sample in terms of reduction
in both porosity and permeability [82 85]. Ahmadi and Shadizadeh [86] evaluated
the ultimate oil recovery factor of nanofluid flooding in carbonate oil reservoirs using
core-displacement experiments. They concluded that adding hydrophilic nanosilica
could considerably increase viscosity of water; increasing viscosity of water means that
sweep efficiency of water is improved. They pointed out the efficiency of nanofluid
increases with nanoparticle content until a certain point and higher concentrations
could not significantly increase the ultimate recovery factor [86].
Kumar and Mandal [87] experimentally studied the performance of carbon dioxide
foam in terms of stability in presence of different nanoparticles as well as different
type of surfactants. They employed nonionic, cationic, and ionic surfactants to
figure out the impact of ionic strength on CO 2 foam stability. Experimental results
revealed that adding nanoparticles could significantly improve the CO 2 foam stability.
Also, they concluded that adding alcohol and polymer resulted in higher stability in
comparison with conventional CO 2 foam system [87]. They presented a possible phe-
nomenon, as shown in Fig. 6.7, to justify their conclusion.
Kumar et al. [88] investigated experimentally the impact of nanoparticles in perfor-
mance of emulsions in terms of thermal stability and viscosity stability. Moreover, they
carried out core-displacement experiments to find the performance of emulsion flooding.
They concluded that nanoparticles improve the performance of emulsions in terms of
both thermal and viscoelastic stability. Also, Pickering emulsion injection resulted in