Page 61 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 61
FIGURE 1.14 Resolution of two sinusoids in frequency, each having a Rayleigh
width of 100 Hz. (a) Well resolved at 500 Hz spacing. (b) Well resolved at 100
Hz spacing. (c) Marginally resolved at 75 Hz spacing. (d) Unresolved at 50 Hz
spacing.
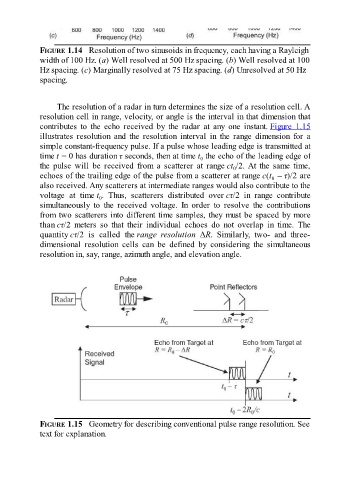
The resolution of a radar in turn determines the size of a resolution cell. A
resolution cell in range, velocity, or angle is the interval in that dimension that
contributes to the echo received by the radar at any one instant. Figure 1.15
illustrates resolution and the resolution interval in the range dimension for a
simple constant-frequency pulse. If a pulse whose leading edge is transmitted at
time t = 0 has duration τ seconds, then at time t the echo of the leading edge of
0
the pulse will be received from a scatterer at range ct /2. At the same time,
0
echoes of the trailing edge of the pulse from a scatterer at range c(t – τ)/2 are
0
also received. Any scatterers at intermediate ranges would also contribute to the
voltage at time t . Thus, scatterers distributed over cτ/2 in range contribute
0
simultaneously to the received voltage. In order to resolve the contributions
from two scatterers into different time samples, they must be spaced by more
than cτ/2 meters so that their individual echoes do not overlap in time. The
quantity cτ/2 is called the range resolution ΔR. Similarly, two- and three-
dimensional resolution cells can be defined by considering the simultaneous
resolution in, say, range, azimuth angle, and elevation angle.
FIGURE 1.15 Geometry for describing conventional pulse range resolution. See
text for explanation.