Page 260 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 260
OILWELL TESTING 197
kh *
t
p D(MBH) ( DA ) = 0.01416 qB o ( p − p ) (7.58)
µ
*
and, since p has been determined in step 1), then pcan be directly calculated. It
should be noted that the MBH charts are equally appropriate for values of t DA and
p D(MBH) evaluated in either Darcy or field units since both parameters are
dimensionless.
9
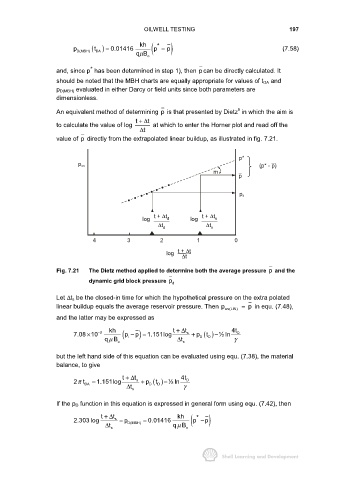
An equivalent method of determining p is that presented by Dietz in which the aim is
t +∆ t
to calculate the value of log at which to enter the Horner plot and read off the
t ∆
value of p directly from the extrapolated linear buildup, as illustrated in fig. 7.21.
p*
(p* - p)
p ws
m
p
p d
log t + ∆t d log t + ∆t s
∆t d ∆t s
4 3 2 1 0
log t + ∆t
∆t
Fig. 7.21 The Dietz method applied to determine both the average pressure p and the
dynamic grid block pressure p d
Let ∆t s be the closed-in time for which the hypothetical pressure on the extra polated
linear buildup equals the average reservoir pressure. Then p ws(LIN) = p in equ. (7.48),
and the latter may be expressed as
kh t +∆ t 4t
7.08 10 − 3 ( i ) p = 1.151log s + p () ½ ln D
t
−
×
p −
qB o t ∆ s D D γ
µ
but the left hand side of this equation can be evaluated using equ. (7.38), the material
balance, to give
t +∆ t 4t
2 t DA = 1.151log s + p D () ½ ln− D
t
π
D
t ∆ γ
s
If the p D function in this equation is expressed in general form using equ. (7.42), then
t +∆ t kh *
2.303 log s = p D(MBH) = 0.01416 ( p − p )
t ∆ s q B o
µ