Page 661 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 661
616 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
TABLE 19.3 (continued)
Ct Data for Various Microorganisms and Disinfectants for 2-log (99%) Kill
Conditions Disinfectant
Microorganism pH T (8C) Chlorine Chloramine Ozone ClO 2
E. histolytica 7.0 0–5 400 a
20–29 60 a
8.0 0–5 600 a
20–29 200 a
a
White (1999, pp. 223, 430) at pH 8.2, HOCL ¼ 80%, OCl ¼ 20%.
b
Calculated from ratios using data in upper left Ct data cells.
c
Sobsey (1989, p. 187), Ct(4-log)=2 ¼ Ct(2-log).
d
Doull, 1980, Table B.1, p. 33; Ct calculated from single concentration and time datum for each organism and each pH
condition; all data at T ¼ 58C. Ct calculations corroborated by Ct data from Table II-2 p. 34.
e
Doull, 1980, Table II-3, p. 40.
f
Doull, 1980, Table II-5 for ozone, p. 50; compiled from various references.
g
Doull, 1980, Table II-6 for chlorine dioxide, p. 58.
h
Wastewater Treatment Plant Design, WPCF Manual of Practice No. 8 (1977, p. 380).
i
Lev and Regli (1992).
j
Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., and HDR Engineering, Inc. (1991).
k
Hibler et al. (1987).
l
Estimate of order of magnitude.
m
Li et al. (2001, p. 601).
n
Langlais (1991, p. 228).
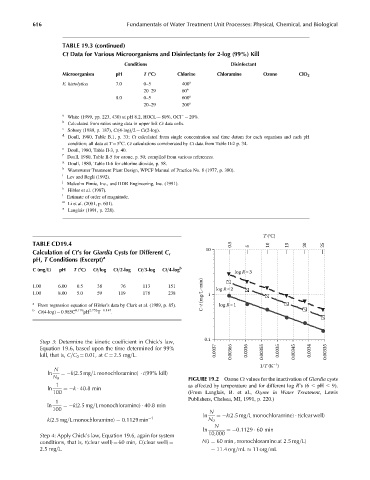
T (°C)
TABLE CD19.4 0.5 10 15 20 25
10 5
Calculation of Ct’s for Giardia Cysts for Different C,
pH, T Conditions (Excerpt) a
C (mg=L) pH T (8C) Ct=log Ct=2-log Ct=3-log Ct=4-log b log R=3
C t (mg/L min)
1.00 6.00 0.5 38 76 113 151 log R=2
1.00 8.00 5.0 59 119 178 238 1
a log R=1
From regression equation of Hibler’s data by Clark et al. (1989, p. 85).
b 0.176 2.752 0.147
Ct(4-log) ¼ 0.985C pH T .
0.1
Step 3: Determine the kinetic coefficient in Chick’s law,
Equation 19.6, based upon the time determined for 99% 0.0037 0.0036 0.0035 0.0034
kill, that is, C=C 0 ¼ 0.01, at C ¼ 2.5 mg=L. 0.00365 0.00355 0.00345 0.00335
–1
1/T (K )
N
ln ¼ k(2:5mg=L monochloramine) t(99% kill)
N 0 FIGURE 19.2 Ozone Ct values for the inactivation of Giardia cysts
1 as affected by temperature and for different log R’s(6 pH 9).
ln ¼ k 40:8 min
100 (From Langlais, B. et al., Ozone in Water Treatment, Lewis
Publishers, Chelsea, MI, 1991, p. 220.)
1
ln ¼ k(2:5mg=L monochloramine) 40:8 min
100 N
ln ¼ k(2:5mg=L monochloramine) t(clear well)
k(2:5mg=L monochloramine) ¼ 0:1129 min 1 N 0
N
ln ¼ 0:1129 60 min
Step 4: Apply Chick’s law, Equation 19.6, again for system 10,000
N(t ¼ 60 min , monochloramine at 2:5mg=L)
conditions, that is, t(clear well) ¼ 60 min, C(clear well) ¼
2.5 mg=L. ¼ 11:4 org=mL 11 org=mL