Page 783 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 783
738 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
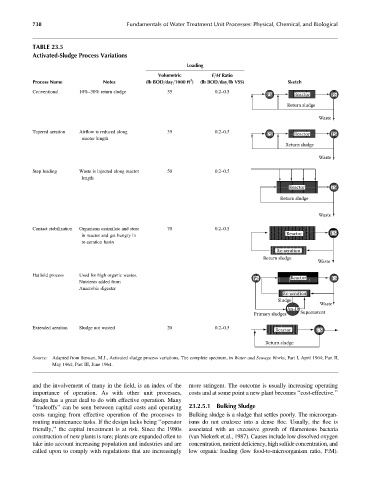
TABLE 23.5
Activated-Sludge Process Variations
Loading
Volumetric F=M Ratio
3
Process Name Notes (lb BOD=day=1000 ft ) (lb BOD=day=lb VSS) Sketch
Conventional 10%–30% return sludge 35 0.2–0.5
PS Reactor FS
Return sludge
Waste
Tapered aeration Airflow is reduced along 35 0.2–0.5
PS Reactor FS
reactor length
Return sludge
Waste
Step loading Waste is injected along reactor 50 0.2–0.5
length
Reactor FS
Return sludge
Waste
Contact stabilization Organisms assimilate and store 70 0.2–0.5
Reactor FS
in reactor and get hungry in
re-aeration basin
Re-aeration
Return sludge
Waste
Hatfield process Used for high organic wastes.
PS Reactor FS
Nutrients added from
Anaerobic digester
Re-aeration
Sludge
Waste
An-D
Primary sludges Supernatent
Extended aeration Sludge not wasted 20 0.2–0.5
Reactor FS
Return sludge
Source: Adapted from Stewart, M.J., Activated sludge process variations, The complete spectrum, in Water and Sewage Works, Part I, April 1964; Part II,
May 1964; Part III, June 1964.
and the involvement of many in the field, is an index of the more stringent. The outcome is usually increasing operating
importance of operation. As with other unit processes, costs and at some point a new plant becomes ‘‘cost-effective.’’
design has a great deal to do with effective operation. Many
‘‘tradeoffs’’ can be seen between capital costs and operating 23.2.5.1 Bulking Sludge
costs ranging from effective operation of the processes to Bulking sludge is a sludge that settles poorly. The microorgan-
routing maintenance tasks. If the design lacks being ‘‘operator isms do not coalesce into a dense floc.Usually,the floc is
friendly,’’ the capital investment is at risk. Since the 1980s associated with an excessive growth of filamentous bacteria
construction of new plants is rare; plants are expanded often to (van Niekerk et al., 1987). Causes include low dissolved oxygen
take into account increasing population and industries and are concentration, nutrient deficiency, high sulfide concentration, and
called upon to comply with regulations that are increasingly low organic loading (low food-to-microorganism ratio, F:M).