Page 185 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 185
172 Gas Purijkation
Design criteria for LPG water wash systems are reviewed by Stewart and Lanning (1991,
1994AI B). For a gravity settler as shown in Figure 2-96, they recommend LPG and wash
water residence times of 15 and 20 minutes, respectively. They also recommend that the
water make-up rate be set to produce a wash water purge to the amine system containing
about 3 wt% amine. Although solubility data such as those of Veldman (1989) can be used
to estimate amine solubility losses in the LPG, it is probably better to use an experience fac-
tor, such as on 0.02 lb of amine per bane1 of LPG feed (about 100 ppmw), as this figure
includes amine entrainment. Note that poorly designed systems with high superficial veloci-
ties or with inadequate LPG residence times in the LPG amine contactor can have amine
losses as high as 500 ppmw (Veldman, 1989). While there is considerable variation, typical
practice is to set the volumetric ratio of wash water to LPG at 1:4, although Stewart and Lan-
ning (1991, 1994B) report on a liquid ethane treater where the wash water was only 6 to 7%
of the LPG volumetric flow. See Table 2-34 for details.
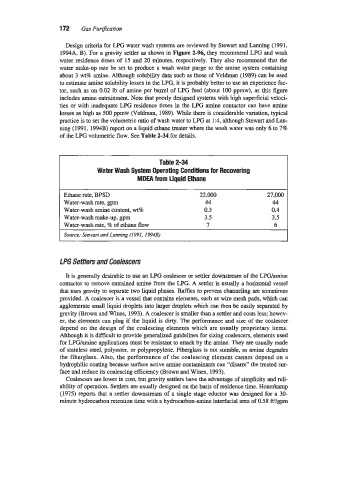
Table 2-34
Water Wash System Operating Conditions for Recovering
MDEA from Liquid Ethane
Ethane rate, BPSD 22,000 27,000
Water-wash rate, gpm 44 44
Water-wash amine content, wt% 0.3 0.4
Water-wash make-up: gpm 3.5 3.5
Water-wash rate, 9 of ethane flow 7 6
w a r t and Lanning (1991.1994B)
LPG Settlers and Coalescers
It is generally desirable to use an LPG coalescer or settler downstream of the LPG/amine
contactor to remove entrained amine from the LPG. A settler is usually a horizontal vessel
that uses gravity to separate two liquid phases. Baffles to prevent channeling are sometimes
provided. A coalescer is a vessel that contains elements, such as wire mesh pads, which can
agglomerate small liquid droplets into larger droplets which can then be easily separated by
gravity (Brown and Wines, 1993). A coalescer is smaller than a settler and costs less; howev-
er, the elements can plug if the liquid is dirty. The performance and size of the coalescer
depend on the design of the coalescing elements which are usually proprietary items.
Although it is difficult to provide generalized guidelines for sizing coalescers, elements used
for LPG/amine applications must be resistant to attack by the amine. They are usually made
of stainless steel, polyester, or polypropylene. Fiberglass is not suitable, as amine degrades
the fiberglass. Also, the performance of the coalescing element cannot depend on a
hydrophilic coating because surface active amine contaminants can “disarm” the treated sur-
face and reduce its coalescing efficiency (Brown and Wines, 1993).
Coalescers are lower in cost, but gravity settlers have the advantage of simplicity and reli-
ability of operation. Settlers are usually designed on the basis of residence time. Honerkamp
(1975) reports that a settler downstream of a single stage eductor was designed for a 30-
minute hydrocarbon retention time with a hydrocarbon-amine interfacial area of 0.58 ftVgpm