Page 258 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 258
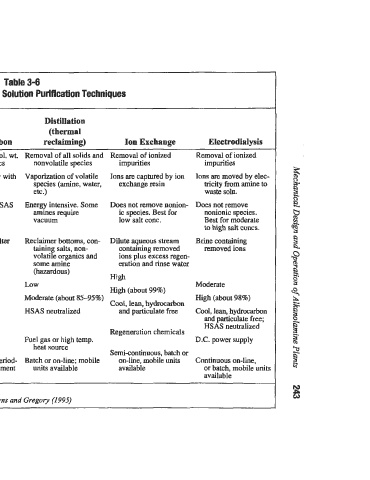
Table 3-6
Comparison of Amine Solution Purlfication Techniques
Distillation
Mechanical (thermal
Filtration Activated Carbon reclaiming) Ion Exchange Electrodialysis
Application Removal of particles and Removal of high mol. wt. Removal of all solids and Removal of ionized Removal of ionized
nonvolatile species
impuntie$
sludge
and polar organics
impurities
Operating principle Filtration Adsorption (usually with Vaporization of volatile Ions am captured by ion Ions are moved by elec-
filtration) species (amine, water, exchange resin tricity from amine to
etc.) waste soh.
Limitations Removes only paaiculate Does not remove HSAS Energy intensiye. Some Does not remove nonion- Does not remove
matter amines requlre ic species. Best for nonionic species.
vacuum low salt conc. Best for moderate
to high salt concs.
Waste products Filter sludge, filter bags, Spent carbon and filter Reclaimer bottoms, con- Dilute aqueous stream Brine containing
and cartridges waste products taining salts, non- containing removed removed ions
(hazardous) (hazardous) volatile qrganics and ions plus excess regen-
some amine eration and rinse water
(hazardous)
High -
Volume of wastes LOW LOW LOW High (about 99%) Moderate
Amine recovery High High Moderate (about 85-9591 High (about 98%)
Cool, lean, hydrocarbon
Amine feed None (lean) Prefiltered lean HSAS neutralized and particulate free Cool, lean, hydrocarbon
requirements and particulate free;
Regeneration chemicals HSAS neutralized
I
Spid None None Fuel gas or high temp. D.C. power supply
requirements heat source
Semi-continuous, batch or
Operating mode Semi-continuous; period- Semi-continuous; period- Batch or on-line; mobile on-line, mobile units Continuous on-line,
ic clean-out required ic carbon replacement units available available or batch, mobile units
required a v ai 1 ab 1 e
~~
Note: HSAS = Heat-stable amine salts.
Source: Data on Ion Exchange, DistiIlution, and Electmdiulysis from Burns and Gregory (1995)