Page 254 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 254
240 Gas Purification
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1 .o
0.5
0.0
CONTACT TIME, HOURS
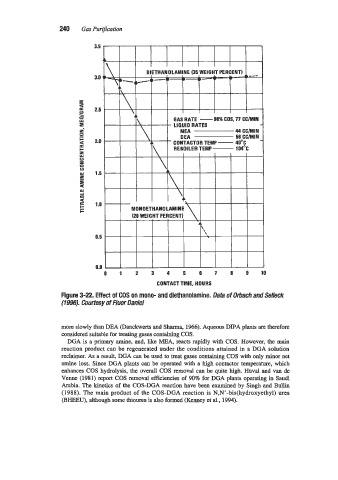
Figure 3-22. Effect of COS on mono- and diethanolamine. Data of Orbach and Selleck
(19%'). Courtesy of Fluor Daniel
more slowly than DEA (Danckwerts and Sharma, 1966). Aqueous DIPA plants are therefore
considered suitable for treating gases containing COS.
DGA is a primary amine, and, like MEA, reacts rapidly with COS. However, the main
reaction product can be regenerated under the conditions attained in a DGA solution
reclaimer. As a result, DGA can be used to treat gases containing COS with only minor net
amine loss. Since DGA plants can be operated with a high contactor temperature, which
enhances COS hydrolysis, the overall COS removal can be quite high. Huval and van de
Venne (1981) report COS removal efficiencies of 90% for DGA plants operating in Saudi
Arabia. The kinetics of the COS-DGA reaction have been examined by Singh and Bullin
(1988). The main product of the COS-DGA reaction is N,N'-bis(hydroxyethy1) urea
(BHEEU), although some thiourea is also formed (Kenney et al., 1994).