Page 270 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 270
254 Gas PuriJcation
the carbon is usually spent before the maximum allowable pressure drop of 30 psi above the
clean bed pressure drop is reached (Leister, 1996). Although steam regeneration has been
used on occasion, in almost all cases the carbon beds are not regenerated since steam is not
effective in removing high-boiling contaminants (Pauley, 1991). When steam regeneration is
used, typical carbon bed life is 4 months after the first cycle, 7 weeks after the second cycle,
and 3 to 4 weeks after the third cycle. Low pressure steam can be used for regeneration, but
must be superheated to 500°F to remove high-boiling contaminants (Schierman, 1973A, B).
Activated carbon filters are often supplied as skid mounted units by carbon vendors such as
the Calgon Carbon Co. of Pittsburgh, PA, and, for larger systems, vendors will often assume
responsibility for carbon replacement and disposal.
4 x 10 Mesh High-DensiiyActivated Canbon Filter
The Perry Equipment Co. of Mineral Wells, TX, has marketed a 4 x 10 mesh activated car-
bon amine filter since the 1970s. Early versions of this filter utilized a wood-based, low-density
activated carbon and were designed for a flux of 10 gpm/ft2 with a minimum bed height of 5
feet (Perry, 1971; 1974; 1980). Recent designs utilize a 4 x 10 mesh, high-density, coal-based
activated carbon (Bums, 1996). The filters are designed for a flux of 10 gpm/@ and the bed
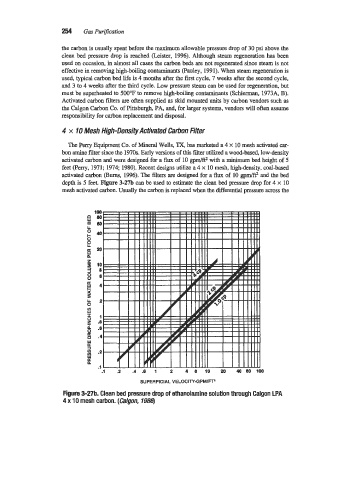
depth is 5 feet. Figure 3-2713 can be used to estimate the clean bed pressure drop for 4 x 10
mesh activated carbon. Usually the carbon is replaced when the differential pressure across the
iii
m
8
B
n.
8
3
I
$2
z
4
P
W
a
3
u)
Y
a
n
SUPERFICIAL VELOCITY-GPMIFT'
Figure 3-27b. Clean bed pressure drop of ethanolamine solution through Calgon LPA
4 x 10 mesh carbon. (Ca/gon, 1986)