Page 141 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 141
Effect of Gas Wettability on the Surface Properties CHAPTER 4 125
4.1.1.3 ADSORPTION ISOTHERM
4.1.1.3.1 Adsorption Isotherm Classification
The experiment shows that the adsorption capacity is related to temperature
and pressure of gas, when a balance is achieved for a certain system. It is
shown using the following formula:
q 5 fðT; pÞ (4.2)
There are, in total, three variables in the above formula. In order to work out
their rules, a variable is always fixed, and the relationship between the other
two variables is resolved.
If T 5 constant, then q 5 f (p), is called adsorption isotherm
If p 5 constant, then q 5 f (T), is called adsorption isobar
If q 5 constant, then p 5 f (T), is called adsorption isostere
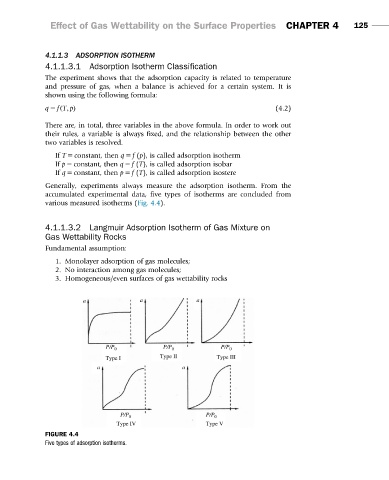
Generally, experiments always measure the adsorption isotherm. From the
accumulated experimental data, five types of isotherms are concluded from
various measured isotherms (Fig. 4.4).
4.1.1.3.2 Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm of Gas Mixture on
Gas Wettability Rocks
Fundamental assumption:
1. Monolayer adsorption of gas molecules;
2. No interaction among gas molecules;
3. Homogeneous/even surfaces of gas wettability rocks
FIGURE 4.4
Five types of adsorption isotherms.