Page 146 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 146
130 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
Table 4.3 CH 4 Adsorption Capacity on Various Wettability Quartz Sands
Water-wetting Quartz Sand Gas-wetting Quartz Sand
Equilibrium Adsorption Equilibrium Adsorption
3
3
Pressure (MPa) Capacity (m /t) Pressure (MPa) Capacity (m /t)
0.00 0.00000 0.00 0.00000
1.36 0.00070 1.24 0.00000
2.54 0.13549 2.31 0.00480
4.05 0.13722 3.64 0.00925
5.69 0.19423 4.78 0.04634
6.58 0.19931 5.47 0.08537
Table 4.4 Comparison of CH 4 Adsorption Capacity of Quartz Sand and
Fine Coal
Water-wetting Quartz Sand Fine Coal
Equilibrium Adsorption Equilibrium Adsorption
3
3
Pressure (MPa) Capacity (m /t) Pressure (MPa) Capacity (m /t)
0.00 0.00000 0.00 0.00000
1.36 0.00070 0.79 1.93189
2.54 0.13549 1.79 3.50931
4.05 0.13722 2.74 4.50770
5.69 0.19423 3.74 5.41357
6.58 0.19931 4.69 6.25737
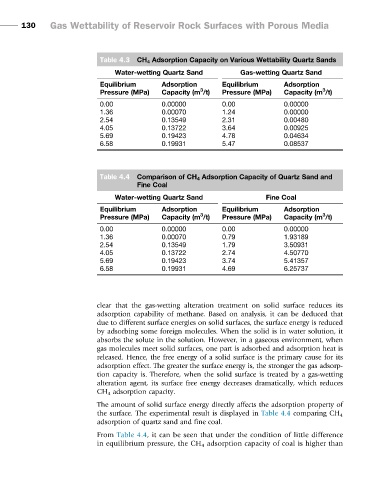
clear that the gas-wetting alteration treatment on solid surface reduces its
adsorption capability of methane. Based on analysis, it can be deduced that
due to different surface energies on solid surfaces, the surface energy is reduced
by adsorbing some foreign molecules. When the solid is in water solution, it
absorbs the solute in the solution. However, in a gaseous environment, when
gas molecules meet solid surfaces, one part is adsorbed and adsorption heat is
released. Hence, the free energy of a solid surface is the primary cause for its
adsorption effect. The greater the surface energy is, the stronger the gas adsorp-
tion capacity is. Therefore, when the solid surface is treated by a gas-wetting
alteration agent, its surface free energy decreases dramatically, which reduces
CH 4 adsorption capacity.
The amount of solid surface energy directly affects the adsorption property of
the surface. The experimental result is displayed in Table 4.4 comparing CH 4
adsorption of quartz sand and fine coal.
From Table 4.4, it can be seen that under the condition of little difference
in equilibrium pressure, the CH 4 adsorption capacity of coal is higher than