Page 149 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 149
Effect of Gas Wettability on the Surface Properties CHAPTER 4 133
Although experimental potential function methods can calculate the interac-
tion potential among molecules, the quantum chemistry method is more
stringent and has no need for any experimental parameter. That is, it can more
precisely calculate weak interaction among molecules [13]. In 2000, Chen
Guochang et al. designed a simple model to replace the surface structure of
coal, and calculated the adsorption potential well of the model and methane,
achieving good results [14]. Based on Chen Changguo’s simplified model, this
section studies fluid adsorption capacity of different wettability surfaces.
4.1.3.3 ESTABLISHING DIFFERENT WETTABILITY MODELS
4.1.3.3.1 Liquid Wetting Rock Models
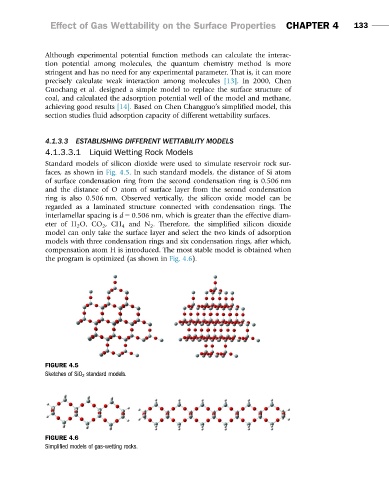
Standard models of silicon dioxide were used to simulate reservoir rock sur-
faces, as shown in Fig. 4.5. In such standard models, the distance of Si atom
of surface condensation ring from the second condensation ring is 0.506 nm
and the distance of O atom of surface layer from the second condensation
ring is also 0.506 nm. Observed vertically, the silicon oxide model can be
regarded as a laminated structure connected with condensation rings. The
interlamellar spacing is d 5 0.506 nm, which is greater than the effective diam-
eter of H 2 O, CO 2 ,CH 4 and N 2 . Therefore, the simplified silicon dioxide
model can only take the surface layer and select the two kinds of adsorption
models with three condensation rings and six condensation rings, after which,
compensation atom H is introduced. The most stable model is obtained when
the program is optimized (as shown in Fig. 4.6).
FIGURE 4.5
Sketches of SiO 2 standard models.
FIGURE 4.6
Simplified models of gas-wetting rocks.