Page 157 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 157
Effect of Gas Wettability on the Surface Properties CHAPTER 4 141
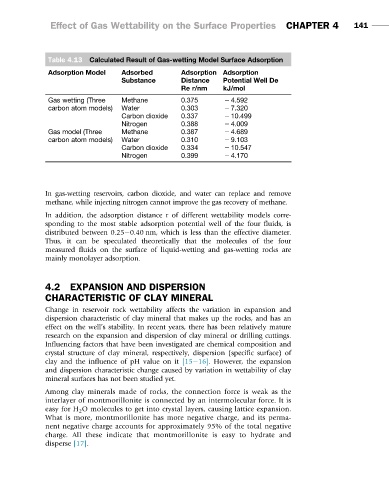
Table 4.13 Calculated Result of Gas-wetting Model Surface Adsorption
Adsorption Model Adsorbed Adsorption Adsorption
Substance Distance Potential Well De
Re r/nm kJ/mol
Gas wetting (Three Methane 0.375 2 4.592
carbon atom models) Water 0.303 2 7.320
Carbon dioxide 0.337 2 10.499
Nitrogen 0.388 2 4.009
Gas model (Three Methane 0.387 2 4.689
carbon atom models) Water 0.310 2 9.103
Carbon dioxide 0.334 2 10.547
Nitrogen 0.399 2 4.170
In gas-wetting reservoirs, carbon dioxide, and water can replace and remove
methane, while injecting nitrogen cannot improve the gas recovery of methane.
In addition, the adsorption distance r of different wettability models corre-
sponding to the most stable adsorption potential well of the four fluids, is
distributed between 0.25 0.40 nm, which is less than the effective diameter.
Thus, it can be speculated theoretically that the molecules of the four
measured fluids on the surface of liquid-wetting and gas-wetting rocks are
mainly monolayer adsorption.
4.2 EXPANSION AND DISPERSION
CHARACTERISTIC OF CLAY MINERAL
Change in reservoir rock wettability affects the variation in expansion and
dispersion characteristic of clay mineral that makes up the rocks, and has an
effect on the well’s stability. In recent years, there has been relatively mature
research on the expansion and dispersion of clay mineral or drilling cuttings.
Influencing factors that have been investigated are chemical composition and
crystal structure of clay mineral, respectively, dispersion (specific surface) of
clay and the influence of pH value on it [15 16]. However, the expansion
and dispersion characteristic change caused by variation in wettability of clay
mineral surfaces has not been studied yet.
Among clay minerals made of rocks, the connection force is weak as the
interlayer of montmorillonite is connected by an intermolecular force. It is
easy for H 2 O molecules to get into crystal layers, causing lattice expansion.
What is more, montmorillonite has more negative charge, and its perma-
nent negative charge accounts for approximately 95% of the total negative
charge. All these indicate that montmorillonite is easy to hydrate and
disperse [17].