Page 161 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 161
Effect of Gas Wettability on the Surface Properties CHAPTER 4 145
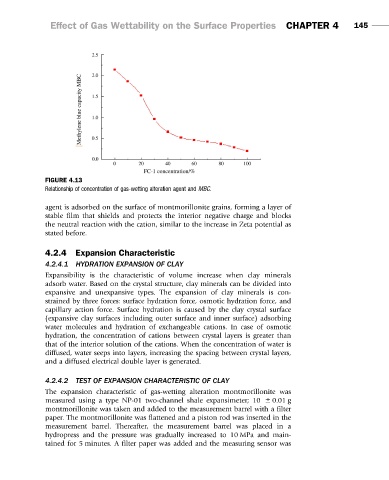
FIGURE 4.13
Relationship of concentration of gas-wetting alteration agent and MBC.
agent is adsorbed on the surface of montmorillonite grains, forming a layer of
stable film that shields and protects the interior negative charge and blocks
the neutral reaction with the cation, similar to the increase in Zeta potential as
stated before.
4.2.4 Expansion Characteristic
4.2.4.1 HYDRATION EXPANSION OF CLAY
Expansibility is the characteristic of volume increase when clay minerals
adsorb water. Based on the crystal structure, clay minerals can be divided into
expansive and unexpansive types. The expansion of clay minerals is con-
strained by three forces: surface hydration force, osmotic hydration force, and
capillary action force. Surface hydration is caused by the clay crystal surface
(expansive clay surfaces including outer surface and inner surface) adsorbing
water molecules and hydration of exchangeable cations. In case of osmotic
hydration, the concentration of cations between crystal layers is greater than
that of the interior solution of the cations. When the concentration of water is
diffused, water seeps into layers, increasing the spacing between crystal layers,
and a diffused electrical double layer is generated.
4.2.4.2 TEST OF EXPANSION CHARACTERISTIC OF CLAY
The expansion characteristic of gas-wetting alteration montmorillonite was
measured using a type NP-01 two-channel shale expansimeter; 10 6 0.01 g
montmorillonite was taken and added to the measurement barrel with a filter
paper. The montmorillonite was flattened and a piston rod was inserted in the
measurement barrel. Thereafter, the measurement barrel was placed in a
hydropress and the pressure was gradually increased to 10 MPa and main-
tained for 5 minutes. A filter paper was added and the measuring sensor was