Page 60 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 60
44 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
This data suggests that the capillary force is a simple, intuitive, and accurate
method. As the result is oil and water wetting of capillary walls, it is normally
used to evaluate the effect of treatment agent and screening treatment agents.
As for defects, it is difficult to select a capillary with uniform radius and obtain
the capillary radius accurately. This method can be used to provide a simple
yet accurate evaluation of gas wettability, but it cannot quantitatively evaluate
gas wettability when the gas wettability is strong.
2.2.2 Evaluation of Gas Wettability by Contact Angle
2.2.2.1 EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
1. The core is first treated with 0.2% lauryl sodium sulfate for 4 hours.
Then it is dried and treated with different concentrations of CTAB solu-
tion for 10 hours, the core is then taken out, and the contact angle of
water phase and oil phase on the surface of the core is measured.
2. The core is first treated with 0.2% lauryl sodium sulfate for 4 hours.
Then it is treated with different concentrations of FC911 solution for
10 hours, and the core is then dried and taken out. The contact angle
of water phase and oil phase on the surface of the core is then
measured.
3. The core is first treated with 0.2% OP-10 for 48 hours. Then it is treated
with FG40 of different concentrations for 10 hours, and the core is then
dried and taken out. Thereafter the contact angle of water phase and oil
phase on the surface of the core is measured.
2.2.2.2 EXPERIMENTAL RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The contact angle method is mainly used for measuring wettability of pure
fluid and artificial core systems. Normally, the wettability of a system is
defined by the angle θ of water on the solid surface. It is generally defined as:
When θ , 75 degrees, it is water-wet. When 75 degrees # θ , 105 degrees, it is
intermediate-wet. When θ $ 105 degrees, it is oil-wet. Through the contact
angle method, the wettability of surface of rock samples treated with three dif-
ferent kinds of surfactants is evaluated. The results are displayed in
Tables 2.1 2.3.
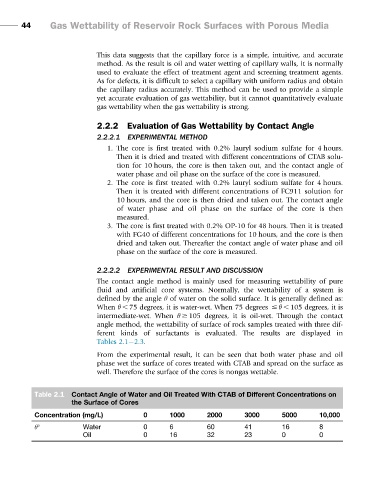
From the experimental result, it can be seen that both water phase and oil
phase wet the surface of cores treated with CTAB and spread on the surface as
well. Therefore the surface of the cores is nongas wettable.
Table 2.1 Contact Angle of Water and Oil Treated With CTAB of Different Concentrations on
the Surface of Cores
Concentration (mg/L) 0 1000 2000 3000 5000 10,000
θ Water 0 6 60 41 16 8
Oil 0 16 32 23 0 0