Page 55 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 55
Evaluation Methods and Influencing Factors CHAPTER 2 39
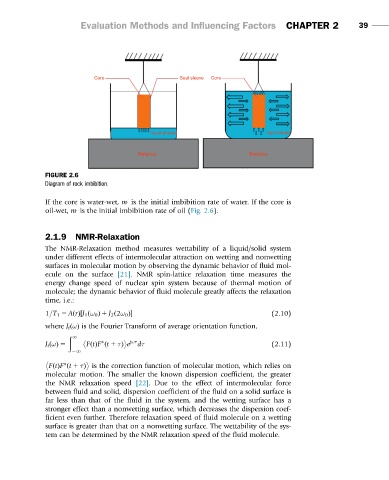
Core Seal sleeve Core
liquid phase liquid phase
Balance Balance
FIGURE 2.6
Diagram of rock imbibition.
:
If the core is water-wet, m is the initial imbibition rate of water. If the core is
:
oil-wet, m is the initial imbibition rate of oil (Fig. 2.6).
2.1.9 NMR-Relaxation
The NMR-Relaxation method measures wettability of a liquid/solid system
under different effects of intermolecular attraction on wetting and nonwetting
surfaces in molecular motion by observing the dynamic behavior of fluid mol-
ecule on the surface [21]. NMR spin-lattice relaxation time measures the
energy change speed of nuclear spin system because of thermal motion of
molecule; the dynamic behavior of fluid molecule greatly affects the relaxation
time, i.e.:
1=T 1 5 ArðÞ J 1 ω 0 Þ 1 J 2 2ω 0 Þ (2.10)
ð
½
ð
where J i ωðÞ is the Fourier Transform of average orientation function,
ð N
J i ωðÞ 5
FtðÞF t 1 τÞ e jωτ dτ (2.11)
ð
2N
FtðÞF t 1 τÞ is the correction function of molecular motion, which relies on
ð
molecular motion. The smaller the known dispersion coefficient, the greater
the NMR relaxation speed [22]. Due to the effect of intermolecular force
between fluid and solid, dispersion coefficient of the fluid on a solid surface is
far less than that of the fluid in the system, and the wetting surface has a
stronger effect than a nonwetting surface, which decreases the dispersion coef-
ficient even further. Therefore relaxation speed of fluid molecule on a wetting
surface is greater than that on a nonwetting surface. The wettability of the sys-
tem can be determined by the NMR relaxation speed of the fluid molecule.