Page 139 - Geochemistry of Oil Field Waters
P. 139
DETERMINING A SOUGHT COMPOUND 127
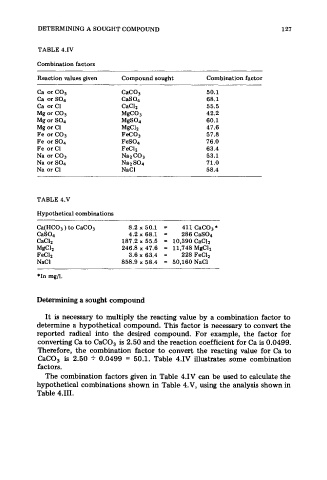
TABLE 4.IV
Combination factors
Reaction values given Compound sought Combination factor
Ca orC03 CaC03 50.1
Ca or SO4 CaS04 68.1
Ca or C1 CaClz 55.5
Mg or C03 MgCO3 42.2
Mg or SO4 MgS04 60.1
Mg or C1 MgClz 47.6
Fe or C03 FeC03 57.8
Fe orS04 FeS04 76.0
Fe orC1 Fa12 63.4
Na or C03 Na~C03 53.1
Na or SO4 Naz SO4 71.0
Na or C1 NaCl 58.4
TABLE 4.V
Hypothetical combinations
Ca(HC03 ) to CaC03 8.2 x 50.1 = 411 CaC03*
CaS04 4.2~ 68.1 = 286CaS04
CaC12 187.2 x 55.5 = 10,390 CaC12
MgCh 246.8 x 47.6 = 11,748 MgClz
FeClz 3.6 x 63.4 = 228 FeCIz
NaCl 858.9 x 58.4 = 50,160 NaCl
*In mg/l.
Determining a sought compound
It is necessary to multiply the reacting value by a combination factor to
determine a hypothetical compound. This factor is necessary to convert the
reported radical into the desired compound. For example, the factor for
converting Ca to CaCO, is 2.50 and the reaction coefficient for Ca is 0.0499.
Therefore, the combination factor to convert the reacting value for Ca to
CaCO, is 2.50 + 0.0499 = 50.1. Table 4.IV illustrates some combination
factors.
The combination factors given in Table 4.IV can be used to calculate the
hypothetical combinations shown in Table 4.V, using the analysis shown in
Table 4.111.