Page 223 - Geometric Modeling and Algebraic Geometry
P. 223
226 M. Shalaby and B. J¨uttler
2
6
1.8
1.6
4
1.4
1.2 2
1
0
0.8
0.6
–2
0.4
0.2 –4
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 –4 –2 0 2 4 6
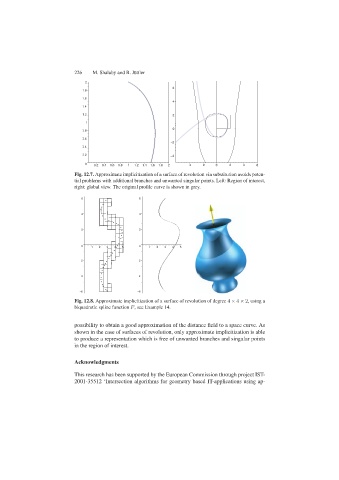
Fig. 12.7. Approximate implicitization of a surface of revolution via substitution avoids poten-
tial problems with additional branches and unwanted singular points. Left: Region of interest,
right: global view. The original profile curve is shown in grey.
6 6
4 4
2 2
0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5
–2 –2
–4 –4
–6 –6
Fig. 12.8. Approximate implicitization of a surface of revolution of degree 4 × 4 × 2, using a
biquadratic spline function F, see Example 14.
possibility to obtain a good approximation of the distance field to a space curve. As
shown in the case of surfaces of revolution, only approximate implicitization is able
to produce a representation which is free of unwanted branches and singular points
in the region of interest.
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by the European Commission through project IST-
2001-35512 ‘Intersection algorithms for geometry based IT-applications using ap-