Page 209 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 209
Soil Water
204 Geotechnical Engineering
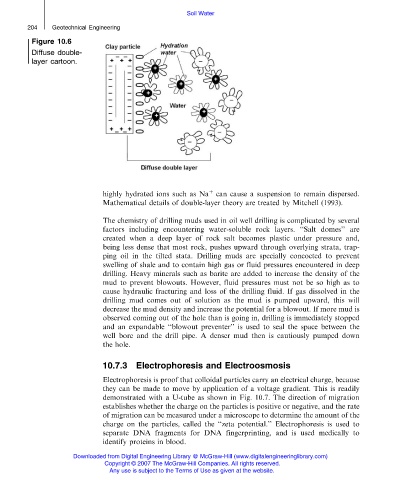
Figure 10.6
Diffuse double-
layer cartoon.
þ
highly hydrated ions such as Na can cause a suspension to remain dispersed.
Mathematical details of double-layer theory are treated by Mitchell (1993).
The chemistry of drilling muds used in oil well drilling is complicated by several
factors including encountering water-soluble rock layers. ‘‘Salt domes’’ are
created when a deep layer of rock salt becomes plastic under pressure and,
being less dense that most rock, pushes upward through overlying strata, trap-
ping oil in the tilted stata. Drilling muds are specially concocted to prevent
swelling of shale and to contain high gas or fluid pressures encountered in deep
drilling. Heavy minerals such as barite are added to increase the density of the
mud to prevent blowouts. However, fluid pressures must not be so high as to
cause hydraulic fracturing and loss of the drilling fluid. If gas dissolved in the
drilling mud comes out of solution as the mud is pumped upward, this will
decrease the mud density and increase the potential for a blowout. If more mud is
observed coming out of the hole than is going in, drilling is immediately stopped
and an expandable ‘‘blowout preventer’’ is used to seal the space between the
well bore and the drill pipe. A denser mud then is cautiously pumped down
the hole.
10.7.3 Electrophoresis and Electroosmosis
Electrophoresis is proof that colloidal particles carry an electrical charge, because
they can be made to move by application of a voltage gradient. This is readily
demonstrated with a U-tube as shown in Fig. 10.7. The direction of migration
establishes whether the charge on the particles is positive or negative, and the rate
of migration can be measured under a microscope to determine the amount of the
charge on the particles, called the ‘‘zeta potential.’’ Electrophoresis is used to
separate DNA fragments for DNA fingerprinting, and is used medically to
identify proteins in blood.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.