Page 191 - Global Tectonics
P. 191
CONTINENTAL RIFTS AND RIFTED MARGINS 177
(a) Tectonic stretching (c)
C MPa
0 1000 0 800
0 0
Temp Yield 2
stress 20 Heat flow = 40 mW m
Crust 20
Mantle 40 Depth (km) 40 Magma Stretch
Depth (km) 60 60
80
Lithosphere
80
Asthenosphere 100
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Stress difference (MPa)
(d)
30
(b) Magmatic extension
C MPa 25
0 1000 0 800
0 20 Stretch
Temp Yield
stress
Crust 20 Tectonic Force (TeraNt/m) 15
Mantle Dike 40 10 Magma
Depth (km) 60 5 0
Lithosphere 80 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
2
Heat flow (mW m )
Asthenosphere
Straining VE = 2
region 40 km
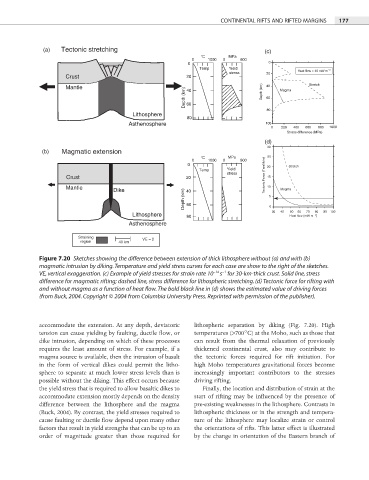
Figure 7.20 Sketches showing the difference between extension of thick lithosphere without (a) and with (b)
magmatic intrusion by diking. Temperature and yield stress curves for each case are show to the right of the sketches.
−14 −1
VE, vertical exaggeration. (c) Example of yield stresses for strain rate 10 s for 30-km-thick crust. Solid line, stress
difference for magmatic rifting; dashed line, stress difference for lithospheric stretching. (d) Tectonic force for rifting with
and without magma as a function of heat flow. The bold black line in (d) shows the estimated value of driving forces
(from Buck, 2004. Copyright © 2004 from Columbia University Press. Reprinted with permission of the publisher).
accommodate the extension. At any depth, deviatoric lithospheric separation by diking (Fig. 7.20). High
tension can cause yielding by faulting, ductile fl ow, or temperatures (>700°C) at the Moho, such as those that
dike intrusion, depending on which of these processes can result from the thermal relaxation of previously
requires the least amount of stress. For example, if a thickened continental crust, also may contribute to
magma source is available, then the intrusion of basalt the tectonic forces required for rift initiation. For
in the form of vertical dikes could permit the litho- high Moho temperatures gravitational forces become
sphere to separate at much lower stress levels than is increasingly important contributors to the stresses
possible without the diking. This effect occurs because driving rifting.
the yield stress that is required to allow basaltic dikes to Finally, the location and distribution of strain at the
accommodate extension mostly depends on the density start of rifting may be influenced by the presence of
difference between the lithosphere and the magma pre-existing weaknesses in the lithosphere. Contrasts in
(Buck, 2004). By contrast, the yield stresses required to lithospheric thickness or in the strength and tempera-
cause faulting or ductile flow depend upon many other ture of the lithosphere may localize strain or control
factors that result in yield strengths that can be up to an the orientations of rifts. This latter effect is illustrated
order of magnitude greater than those required for by the change in orientation of the Eastern branch of