Page 65 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 65
An extended illustration 63
An extended illustration
In this section, we discuss the design and results of two previously published studies
[18,54,76,92] that illustrate the approach introduced in Accuracy and its conse-
quences section. The goals of the project were (1) to assess how different aspects
of a BGM system accuracy affect HbA1c, severe hypoglycemia, insulin, and finger-
stick use (and costs); and (2) understand how the BGM system accuracy affects
long-term financial costs to the patient and the health system. A BGM system
includes the meter as well as the strips (both can cause inaccuracy). The project
was constrained to type 1 diabetes patients using CSII. The general approach
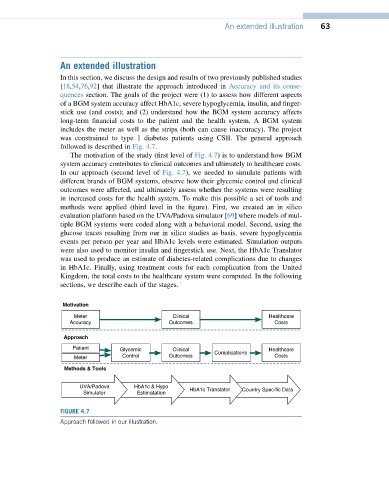
followed is described in Fig. 4.7.
The motivation of the study (first level of Fig. 4.7) is to understand how BGM
system accuracy contributes to clinical outcomes and ultimately to healthcare costs.
In our approach (second level of Fig. 4.7), we needed to simulate patients with
different brands of BGM systems, observe how their glycemic control and clinical
outcomes were affected, and ultimately assess whether the systems were resulting
in increased costs for the health system. To make this possible a set of tools and
methods were applied (third level in the figure). First, we created an in silico
evaluation platform based on the UVA/Padova simulator [69] where models of mul-
tiple BGM systems were coded along with a behavioral model. Second, using the
glucose traces resulting from our in silico studies as basis, severe hypoglycemia
events per person per year and HbA1c levels were estimated. Simulation outputs
were also used to monitor insulin and fingerstick use. Next, the HbA1c Translator
was used to produce an estimate of diabetes-related complications due to changes
in HbA1c. Finally, using treatment costs for each complication from the United
Kingdom, the total costs to the healthcare system were computed. In the following
sections, we describe each of the stages.
Motivation
Meter Clinical Healthcare
Accuracy Outcomes Costs
Approach
Patient Glycemic Clinical Healthcare
Complications
Meter Control Outcomes Costs
Methods & Tools
UVA/Padova HbA1c & Hypo HbA1c Translator
Simulator Estimatation
FIGURE 4.7
Approach followed in our illustration.