Page 62 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 62
60 CHAPTER 4 Consequences of SMBG systems inaccuracy
Glucose
Reading
Carb & Insulin
Traces
true glucose
Meal carbs Metabolic Meter
Behavior Model Model
awareness
model simulated
insulin rescue reading
carbs
Insulin Behavioral
Pump
bolus Model
Model
decision
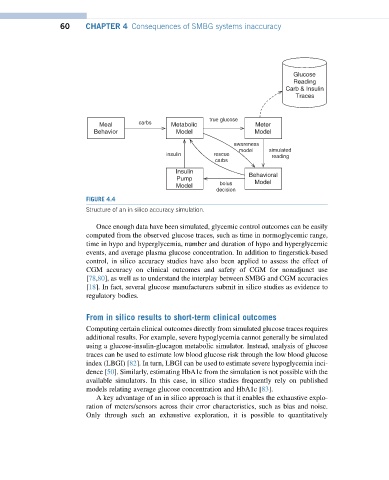
FIGURE 4.4
Structure of an in silico accuracy simulation.
Once enough data have been simulated, glycemic control outcomes can be easily
computed from the observed glucose traces, such as time in normoglycemic range,
time in hypo and hyperglycemia, number and duration of hypo and hyperglycemic
events, and average plasma glucose concentration. In addition to fingerstick-based
control, in silico accuracy studies have also been applied to assess the effect of
CGM accuracy on clinical outcomes and safety of CGM for nonadjunct use
[78,80], as well as to understand the interplay between SMBG and CGM accuracies
[18]. In fact, several glucose manufacturers submit in silico studies as evidence to
regulatory bodies.
From in silico results to short-term clinical outcomes
Computing certain clinical outcomes directly from simulated glucose traces requires
additional results. For example, severe hypoglycemia cannot generally be simulated
using a glucose-insulin-glucagon metabolic simulator. Instead, analysis of glucose
traces can be used to estimate low blood glucose risk through the low blood glucose
index (LBGI) [82]. In turn, LBGI can be used to estimate severe hypoglycemia inci-
dence [50]. Similarly, estimating HbA1c from the simulation is not possible with the
available simulators. In this case, in silico studies frequently rely on published
models relating average glucose concentration and HbA1c [83].
A key advantage of an in silico approach is that it enables the exhaustive explo-
ration of meters/sensors across their error characteristics, such as bias and noise.
Only through such an exhaustive exploration, it is possible to quantitatively