Page 67 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 67
An extended illustration 65
Behavioral models
For the purpose of the study, behaviors such as self-treatment of hypoglycemia,
meal, and bolusing were modeled as independent behaviors. The prospective models
were parameterized using clinical data. The models were statistically validated
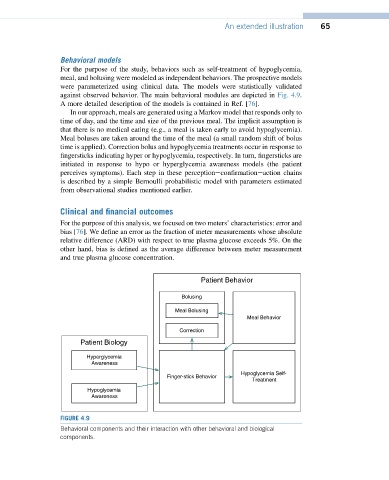
against observed behavior. The main behavioral modules are depicted in Fig. 4.9.
A more detailed description of the models is contained in Ref. [76].
In our approach, meals are generated using a Markov model that responds only to
time of day, and the time and size of the previous meal. The implicit assumption is
that there is no medical eating (e.g., a meal is taken early to avoid hypoglycemia).
Meal boluses are taken around the time of the meal (a small random shift of bolus
time is applied). Correction bolus and hypoglycemia treatments occur in response to
fingersticks indicating hyper or hypoglycemia, respectively. In turn, fingersticks are
initiated in response to hypo or hyperglycemia awareness models (the patient
perceives symptoms). Each step in these perceptioneconfirmationeaction chains
is described by a simple Bernoulli probabilistic model with parameters estimated
from observational studies mentioned earlier.
Clinical and financial outcomes
For the purpose of this analysis, we focused on two meters’ characteristics: error and
bias [76]. We define an error as the fraction of meter measurements whose absolute
relative difference (ARD) with respect to true plasma glucose exceeds 5%. On the
other hand, bias is defined as the average difference between meter measurement
and true plasma glucose concentration.
Patient Behavior
Bolusing
Meal Bolusing
Meal Behavior
Correction
Patient Biology
Hyperglycemia
Awareness
Hypoglycemia Self-
Finger-stick Behavior
Treatment
Hypoglycemia
Awareness
FIGURE 4.9
Behavioral components and their interaction with other behavioral and biological
components.