Page 502 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 502
474 Chapter 11 - Gypsum and Gypsum Products
where f(a) is a function depending on the kinetic model obeyed by the
reaction and A is a pre-exponential factor in the Arrhenius expression for
the rate constant, E is the apparent activation energy, R is the gas constant,
and T is the absolute temperature.
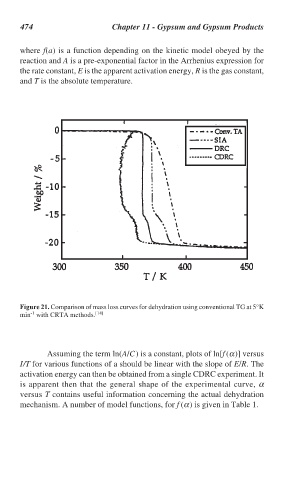
Figure 21. Comparison of mass loss curves for dehydration using conventional TG at 5°K
-1
min with CRTA methods. [14]
Assuming the term ln(A/C) is a constant, plots of ln[f (α)] versus
I/T for various functions of a should be linear with the slope of E/R. The
activation energy can then be obtained from a single CDRC experiment. It
is apparent then that the general shape of the experimental curve, α
versus T contains useful information concerning the actual dehydration
mechanism. A number of model functions, for f (α) is given in Table 1.