Page 774 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 774
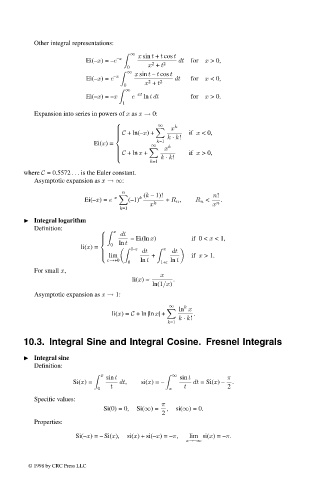
Other integral representations:
∞ x sin t + t cos t
Ei(–x)= –e –x 2 2 dt for x >0,
0 x + t
∞ x sin t – t cos t
Ei(–x)= e –x 2 2 dt for x <0,
0 x + t
∞
Ei(–x)= –x e –xt ln tdt for x >0.
1
Expansion into series in powers of x as x → 0:
∞ k
x
C + ln(–x)+ if x <0,
k ⋅ k!
Ei(x)= k=1
∞ k
x
C +ln x + if x >0,
k ⋅ k!
k=1
where C = 0.5572 ... is the Euler constant.
Asymptotic expansion as x →∞:
n
k (k – 1)! n!
–x
Ei(–x)= e (–1) + R n , R n < .
x k x n
k=1
Integral logarithm
Definition:
x
dt
= Ei(ln x) if 0 < x <1,
ln t
0
li(x)= 1–ε x
dt dt
lim + if x >1.
ε→+0 ln t ln t
0 1+ε
For small x,
li(x) ≈ x .
ln(1/x)
Asymptotic expansion as x → 1:
∞ k
ln x
li(x)= C +ln |ln x| + .
k ⋅ k!
k=1
10.3. Integral Sine and Integral Cosine. Fresnel Integrals
Integral sine
Definition:
x sin t ∞ sin t π
Si(x)= dt, si(x)= – dt = Si(x) – .
0 t x t 2
Specific values:
π
Si(0) = 0, Si(∞)= , si(∞)=0.
2
Properties:
Si(–x)= – Si(x), si(x) + si(–x)= –π, lim si(x)= –π.
x→–∞
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 759