Page 42 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 42
2.10 Hydrogen bonding 35
There many examples of
hydrogen bonding effect on the
mechanical performance of mate-
rials. For example, spider silk and
collagen perform so well because
they transfer loads by hydrogen
68
bond-assisted mechanism. There
are many examples of nanoparti-
cle-matrix interaction which rein-
68
force composites. Figure 2.37
shows that adhesion between
ultrahigh molecular weight poly-
ethylene fibers and epoxy surface
is increased because of hydrogen
bonding between polypyrrole and
fiber and mechanical interlocking
of polypyrrole and epoxy matrix. 68
The hydrogen bonds
(NH– … O=C ) form between
UHMWPE and PPy at the inter-
face. The formation of the hydro-
gen bonds was confirmed by
68
FTIR, DMA, and DSC.
Dimethylnorbornene ester
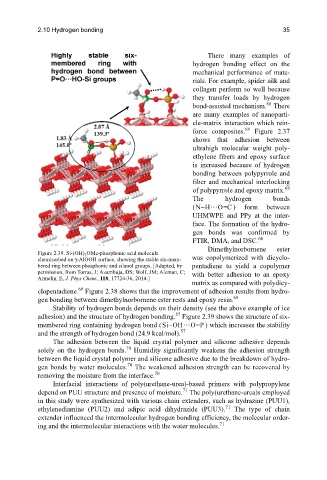
Figure 2.39. Si-(OH) 3 OMe-phosphonic acid molecule
chemisorbed on γ-AlOOH surface, showing the stable six-mem- was copolymerized with dicyclo-
bered ring between phosphonic and silanol groups. [Adapted, by pentadiene to yield a copolymer
permission, from Torras, J; Azambuja, DS; Wolf, JM; Aleman, C; with better adhesion to an epoxy
Armelin, E, J. Phys Chem., 118, 17724-36, 2014.]
matrix as compared with polydicy-
69
clopentadiene. Figure 2.38 shows that the improvement of adhesion results from hydro-
69
gen bonding between dimethylnorbornene ester rests and epoxy resin.
Stability of hydrogen bonds depends on their density (see the above example of ice
57
adhesion) and the structure of hydrogen bonding. Figure 2.39 shows the structure of six-
membered ring containing hydrogen bond (Si OH– … O=P ) which increases the stability
57
and the strength of hydrogen bond (24.9 kcal/mol).
The adhesion between the liquid crystal polymer and silicone adhesive depends
70
solely on the hydrogen bonds. Humidity significantly weakens the adhesion strength
between the liquid crystal polymer and silicone adhesive due to the breakdown of hydro-
70
gen bonds by water molecules. The weakened adhesion strength can be recovered by
70
removing the moisture from the interface.
Interfacial interactions of poly(urethane-urea)-based primers with polypropylene
71
depend on PUU structure and presence of moisture. The poly(urethane-urea)s employed
in this study were synthesized with various chain extenders, such as hydrazine (PUU1),
71
ethylenediamine (PUU2) and adipic acid dihydrazide (PUU3). The type of chain
extender influenced the intermolecular hydrogen bonding efficiency, the molecular order-
71
ing and the intermolecular interactions with the water molecules.