Page 39 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 39
32 Mechanisms of Adhesion
maleic anhydride improved adhesion between the MWCNTs and polymethylmethacry-
59
late. The molecular arrangement of the PMMA matrix was changed and carbon nano-
o
59
tubes were homogeneously distributed. Glass transition temperature (19 C increase) and
59
storage modulus (184% increase) of composites were significantly increased.
60
Polypropylene was reinforced with wood fillers. Interfacial adhesion was changed
by the introduction of maleated polypropylene. Large aspect ratio and small fiber diameter
60
result from better reinforcement. Coupling with functionalized polymer is necessary for
the preparation of composites with acceptable properties if the size of the particles is large
60
and their aspect ratio is small. Maleic anhydride grafted poly(lactic acid) was prepared
61
by reactive processing. The functionalized polymer was an efficient coupling agent for
PLA/wood composites. Fracture of fibers was the dominating local deformation process.
61
Debonding occurs in the neat, uncoupled composites. To prevent debonding, the cou-
61
pling is needed resulting in the improved performance of the composite.
Urea compounds are formed on the surface of metals due to the reaction of adsorbed
62
water with isocyanates. The urea compounds have only physical interaction with the sur-
62
face of metal and they do not contribute to adhesion. The isocyanate groups react with
hydroxide groups on the surface of metals and this reaction plays a significant role in
62
adhesion of polyurethanes to metals. New FTIR bands are formed from reaction (1700
-1 62
and 1400-1150 cm ).
Zinc and copper sulfide surfaces are formed in adhesive interlayer during rubber vul-
63
canization. Cu S surface exhibits higher adsorption energies than CuS surface, which
2
indicates higher role of Cu S, or non-stoichiometric Cu S phases, in the adhesion between
x
2
63
rubber and brass. Zinc sulfide seems to prefer adsorption via sulfur-containing groups,
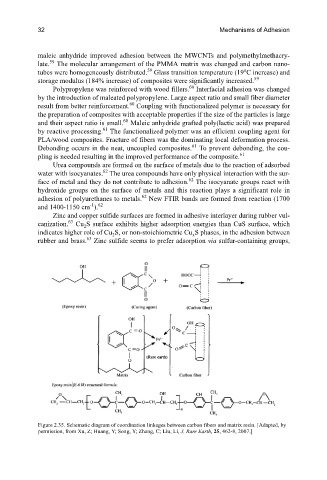
Figure 2.35. Schematic diagram of coordination linkages between carbon fibers and matrix resin. [Adapted, by
permission, from Xu, Z; Huang, Y; Song, Y; Zhang, C; Liu, Li, J. Rare Earth, 25, 462-8, 2007.]