Page 34 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 34
2.8 Interphase formation 27
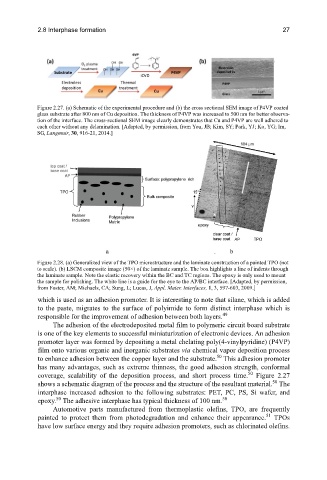
Figure 2.27. (a) Schematic of the experimental procedure and (b) the cross sectional SEM image of P4VP coated
glass substrate after 800 nm of Cu deposition. The thickness of P4VP was increased to 500 nm for better observa-
tion of the interface. The cross-sectional SEM image clearly demonstrates that Cu and P4VP are well adhered to
each other without any delamination. [Adapted, by permission, from You, JB; Kim, SY; Park, YJ; Ko, YG; Im,
SG, Langmuir, 30, 916-21, 2014.]
Figure 2.28. (a) Generalized view of the TPO microstructure and the laminate construction of a painted TPO (not
to scale). (b) LSCM composite image (50×) of the laminate sample. The box highlights a line of indents through
the laminate sample. Note the elastic recovery within the BC and TC regions. The epoxy is only used to mount
the sample for polishing. The white line is a guide for the eye to the AP/BC interface. [Adapted, by permission,
from Foster, AM; Michaels, CA; Sung, L; Lucas, J, Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 1, 3, 597-603, 2009.]
which is used as an adhesion promoter. It is interesting to note that silane, which is added
to the paste, migrates to the surface of polyimide to form distinct interphase which is
49
responsible for the improvement of adhesion between both layers.
The adhesion of the electrodeposited metal film to polymeric circuit board substrate
is one of the key elements to successful miniaturization of electronic devices. An adhesion
promoter layer was formed by depositing a metal chelating poly(4-vinylpyridine) (P4VP)
film onto various organic and inorganic substrates via chemical vapor deposition process
50
to enhance adhesion between the copper layer and the substrate. This adhesion promoter
has many advantages, such as extreme thinness, the good adhesion strength, conformal
50
coverage, scalability of the deposition process, and short process time. Figure 2.27
50
shows a schematic diagram of the process and the structure of the resultant material. The
interphase increased adhesion to the following substrates: PET, PC, PS, Si wafer, and
50
50
epoxy. The adhesive interphase has typical thickness of 100 nm.
Automotive parts manufactured from thermoplastic olefins, TPO, are frequently
51
painted to protect them from photodegradation and enhance their appearance. TPOs
have low surface energy and they require adhesion promoters, such as chlorinated olefins.