Page 29 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 29
22 Mechanisms of Adhesion
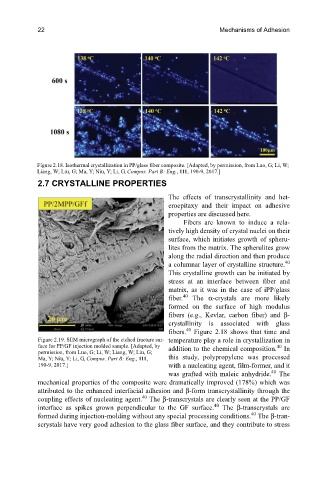
Figure 2.18. Isothermal crystallization in PP/glass fiber composite. [Adapted, by permission, from Luo, G; Li, W;
Liang, W; Liu, G; Ma, Y; Niu, Y; Li, G, Compos. Part B: Eng., 111, 190-9, 2017.]
2.7 CRYSTALLINE PROPERTIES
The effects of transcrystallinity and het-
eroepitaxy and their impact on adhesive
properties are discussed here.
Fibers are known to induce a rela-
tively high density of crystal nuclei on their
surface, which initiates growth of spheru-
lites from the matrix. The spherulites grow
along the radial direction and then produce
a columnar layer of crystalline structure. 40
This crystalline growth can be initiated by
stress at an interface between fiber and
matrix, as it was in the case of iPP/glass
40
fiber. The α-crystals are more likely
formed on the surface of high modulus
fibers (e.g., Kevlar, carbon fiber) and β-
crystallinity is associated with glass
40
fibers. Figure 2.18 shows that time and
Figure 2.19. SEM micrograph of the etched fracture sur- temperature play a role in crystallization in
face for PP/GF injection molded sample. [Adapted, by addition to the chemical composition. In
40
permission, from Luo, G; Li, W; Liang, W; Liu, G;
Ma, Y; Niu, Y; Li, G, Compos. Part B: Eng., 111, this study, polypropylene was processed
190-9, 2017.] with a nucleating agent, film-former, and it
40
was grafted with maleic anhydride. The
mechanical properties of the composite were dramatically improved (178%) which was
attributed to the enhanced interfacial adhesion and β-form transcrystallinity through the
40
coupling effects of nucleating agent. The β-transcrystals are clearly seen at the PP/GF
40
interface as spikes grown perpendicular to the GF surface. The β-transcrystals are
40
formed during injection-molding without any special processing conditions. The β-tran-
scrystals have very good adhesion to the glass fiber surface, and they contribute to stress