Page 33 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 33
26 Mechanisms of Adhesion
46
polymerization. The twin polymerization was performed using the following monomers:
2,20-spirobi-[4H-1,3,2-benzodioxasiline] and 2-(3-amino-n-propyl)-2-methyl-4H-1,3,2-
46
benzodioxasiline. The resultant polymer is very convenient for use as an interphase
because it is produced without shrinkage and formation of low-molecular weight prod-
46
ucts.
Resist lithography is used in the electronics industry as a common microfabrication
47
technique. Epoxy oligomer (SU 8) is a favorite photoresist material but it suffers from
47
poor adhesion to silicon which is used as the common substrate. A layer of polyallylam-
ine was found to be an excellent adhesion promoter because it spontaneously absorbs on
47
silicon and has amine groups reactive with epoxy oligomer. Figure 2.24 shows steps of
47
microfabrication.
Figure 2.25 shows a method
of fabrication of a digital micro-
fluidic chip from poly(p-xylylene)
(Parylene C) and tantalum pentox-
48
ide. Because both layers do not
have sufficient adhesion, the inter-
mediate layer has to be produced
48
to hold them together. This layer
is formed from γ-methacryloxy-
48
propyltrimethoxy silane. During
the coating process, the surface of
Ta O reacts with adsorbed water
5
2
molecules in the air and forms a
48
hydroxyl group, Ta−OH. The
hydroxyl group reacts with silane
forming a self-limited molecular
layer on the Ta O surface (Figure
2
5
48
2.25c). The monomers of
Parylene C deposited on the sur-
face of a polymerized silane (Fig-
ure 2.25b) copolymerize with the
methacryloxy tail via a free radical
addition reaction and deposit as a
48
polymer layer. This technology
leads to the formation of very thin
(monomolecular) interface
48
enhancing adhesion.
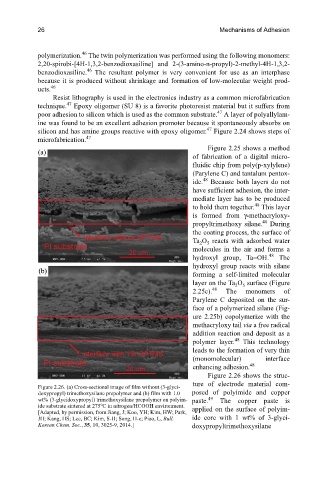
Figure 2.26 shows the struc-
ture of electrode material com-
Figure 2.26. (a) Cross-sectional image of film without (3-glyci-
doxypropyl) trimethoxysilane prepolymer and (b) film with 1.0 posed of polyimide and copper
49
wt% (3-glycidoxypropyl) trimethoxysilane prepolymer on polyim- paste. The copper paste is
o
ide substrate sintered at 275 C in nitrogen/HCOOH environment. applied on the surface of polyim-
[Adapted, by permission, from Jiang, J; Koo, YH; Kim, HW; Park,
JH; Kang, HS; Lee, BC; Kim, S-H; Song, H-e; Piao, L, Bull. ide core with 1 wt% of 3-glyci-
Korean Chem. Soc., 35, 10, 3025-9, 2014.] doxypropyltrimethoxysilane