Page 52 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 52
3
Mechanisms of Adhesion Loss
Here we discuss various pathways to adhesion failure, including
• c o r r o s i o n
• delamination
• detachment
• debonding
• liquid penetration
• peeling
3.1 CORROSION
An anodic reaction, which leads to metal
loss, is an example of the corrosion process.
If metal is lost in the neighborhood of inter-
face with coating, the adhesion between the
metal and its coating is also lost.
Localized anodic reactions on steel or
aluminum can cause oxygen reduction
leading to the cathodic degradation of the
1
adhesive bond. Voluminous corrosion
products provide a mechanical driver for
1
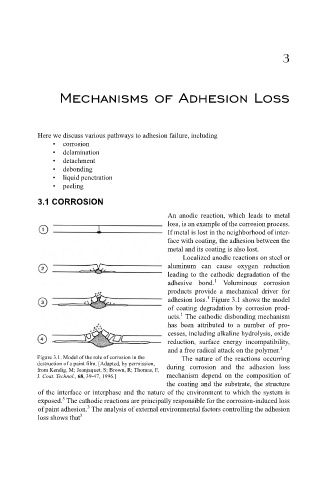
adhesion loss. Figure 3.1 shows the model
of coating degradation by corrosion prod-
1
ucts. The cathodic disbonding mechanism
has been attributed to a number of pro-
cesses, including alkaline hydrolysis, oxide
reduction, surface energy incompatibility,
1
and a free radical attack on the polymer.
Figure 3.1. Model of the role of corrosion in the The nature of the reactions occurring
destruction of a paint film. [Adapted, by permission, during corrosion and the adhesion loss
from Kendig, M; Jeanjaquet, S; Brown, R; Thomas, F,
J. Coat. Technol., 68, 39-47, 1996.] mechanism depend on the composition of
the coating and the substrate, the structure
of the interface or interphase and the nature of the environment to which the system is
3
exposed. The cathodic reactions are principally responsible for the corrosion-induced loss
3
of paint adhesion. The analysis of external environmental factors controlling the adhesion
3
loss shows that