Page 40 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 40
STATICS, STRESS AND STRAIN, AND FLEXURAL ANALYSIS 1.23
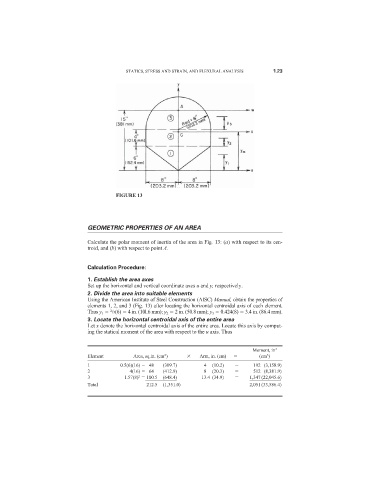
FIGURE 13
GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF AN AREA
Calculate the polar moment of inertia of the area in Fig. 13: (a) with respect to its cen-
troid, and (b) with respect to point A.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Establish the area axes
Set up the horizontal and vertical coordinate axes u and y, respectively.
2. Divide the area into suitable elements
Using the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) Manual, obtain the properties of
elements 1, 2, and 3 (Fig. 13) after locating the horizontal centroidal axis of each element.
2
Thus y 1 /3(6) 4 in. (10l.6 mm); y 2 2 in. (50.8 mm); y 3 0.424(8) 3.4 in. (86.4 mm).
3. Locate the horizontal centroidal axis of the entire area
Let x denote the horizontal centroidal axis of the entire area. Locate this axis by comput-
ing the statical moment of the area with respect to the u axis. Thus
Moment, in 3
2
3
Element Area, sq.in. (cm ) Arm, in. (cm) (cm )
1 0.5(6)(16) 48 (309.7) 4 (10.2) 192 (3,158.9)
2 4(16) 64 (412.9) 8 (20.3) 512 (8,381.9)
2
3 1.57(8) 100.5 (648.4) 13.4 (34.9) 1,347 (22,045.6)
_____________ _____________
Total 212.5 (1,351.0) 2,051 (33,586.4)