Page 43 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 43
1.26 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
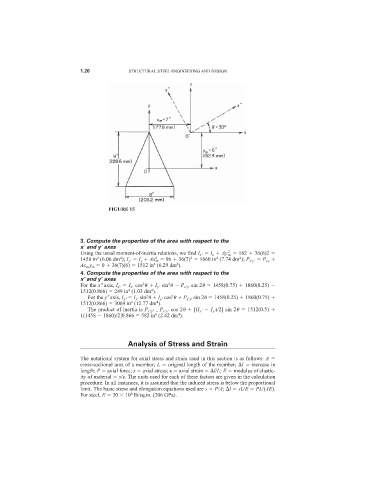
FIGURE 15
3. Compute the properties of the area with respect to the
x
and y
axes
2
Using the usual moment-of-inertia relations, we find I x
I x Ay m 162 36(6)2
4
4
2
4
4
2
1458 in (6.06 dm ); I y
I y Ax m 96 36(7) 1660 in (7.74 dm ); P x
y
P xy
4
4
Ax m y m 0 36(7)(6) 1512 in (6.29 dm ).
4. Compute the properties of the area with respect to the
x and y axes
For the x axis, I x I x
cos I y
sin P x
y
sin 2 1458(0.75) 1860(0.25)
2
2
4
4
1512(0.866) 249 in (1.03 dm ).
2
2
For the y axis, I y I x
sin I y
cos P x
y
sin 2 1458(0.25) 1860(0.75)
4
4
1512(0.866) 3069 in (12.77 dm ).
The product of inertia is P x y P x
y
cos 2 [(I x
I y
)/2] sin 2 1512(0.5)
4
4
1(1458 1860)/2]0.866 582 in (2.42 dm ).
Analysis of Stress and Strain
The notational system for axial stress and strain used in this section is as follows: A
cross-sectional area of a member; L original length of the member; l increase in
length; P axial force; s axial stress;
axial strain l/L; E modulus of elastic-
ity of material s/
. The units used for each of these factors are given in the calculation
procedure. In all instances, it is assumed that the induced stress is below the proportional
limit. The basic stress and elongation equations used are s P/A; l sL/E PL/(AE).
6
For steel, E 30 10 lb/sq.in. (206 GPa).