Page 151 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 151
134 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
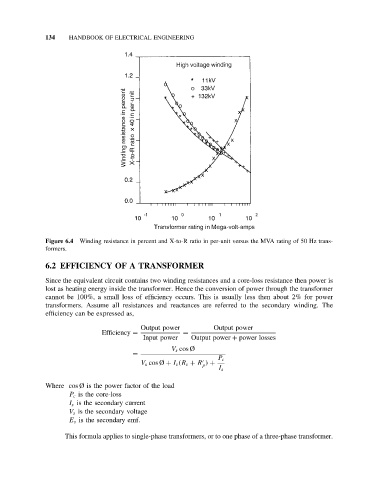
Figure 6.4 Winding resistance in percent and X-to-R ratio in per-unit versus the MVA rating of 50 Hz trans-
formers.
6.2 EFFICIENCY OF A TRANSFORMER
Since the equivalent circuit contains two winding resistances and a core-loss resistance then power is
lost as heating energy inside the transformer. Hence the conversion of power through the transformer
cannot be 100%, a small loss of efficiency occurs. This is usually less then about 2% for power
transformers. Assume all resistances and reactances are referred to the secondary winding. The
efficiency can be expressed as,
Output power Output power
Efficiency = =
Input power Output power + power losses
V s cos Ø
=
P c
V s cos Ø + I s (R s + R ) +
p
I s
Where cos Ø is the power factor of the load
P c is the core-loss
I s is the secondary current
V s is the secondary voltage
E s is the secondary emf.
This formula applies to single-phase transformers, or to one phase of a three-phase transformer.