Page 598 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 598
EARTHING CURRENT AND ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE 591
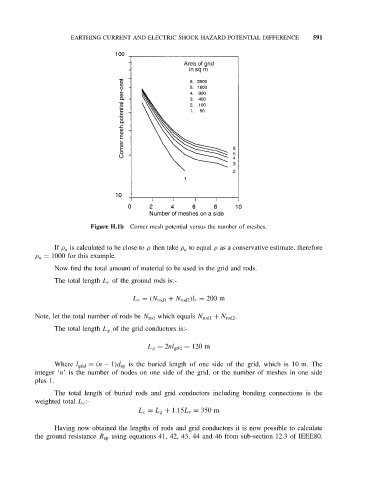
Figure H.1b Corner mesh potential versus the number of meshes.
If ρ a is calculated to be close to ρ then take ρ a to equal ρ as a conservative estimate, therefore
ρ a = 1000 for this example.
Now find the total amount of material to be used in the grid and rods.
The total length L r of the ground rods is:-
L r = (N rod1 + N rod2 )l r = 200 m
Note, let the total number of rods be N rod which equals N rod1 + N rod2 .
The total length L g of the grid conductors is:-
L g = 2nl grid = 120 m
Where l grid = (n − 1)d sp is the buried length of one side of the grid, which is 10 m. The
integer ‘n’ is the number of nodes on one side of the grid, or the number of meshes in one side
plus 1.
The total length of buried rods and grid conductors including bonding connections is the
weighted total L c :-
L c = L g + 1.15L r = 350 m
Having now obtained the lengths of rods and grid conductors it is now possible to calculate
the ground resistance R ep using equations 41, 42, 43, 44 and 46 from sub-section 12.3 of IEEE80.