Page 464 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 464
462 CHAPTER 17 Application of pyrolysis
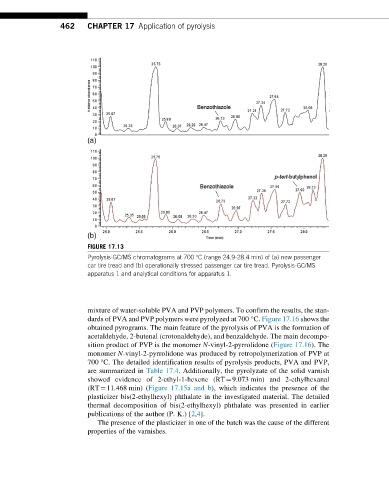
FIGURE 17.13
Pyrolysis-GC/MS chromatograms at 700 °C (range 24.9-28.4 min) of (a) new passenger
car tire tread and (b) operationally stressed passenger car tire tread. Pyrolysis-GC/MS
apparatus 1 and analytical conditions for apparatus 1.
mixture of water-soluble PVA and PVP polymers. To confirm the results, the stan-
dards of PVA and PVP polymers were pyrolyzed at 700 °C. Figure 17.16 shows the
obtained pyrograms. The main feature of the pyrolysis of PVA is the formation of
acetaldehyde, 2-butenal (crotonaldehyde), and benzaldehyde. The main decompo-
sition product of PVP is the monomer N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone (Figure 17.16). The
monomer N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone was produced by retropolymerization of PVP at
700 °C. The detailed identification results of pyrolysis products, PVA and PVP,
are summarized in Table 17.4. Additionally, the pyrolyzate of the solid varnish
showed evidence of 2-ethyl-1-hexene (RT¼9.073 min) and 2-ethylhexanal
(RT¼11.468 min) (Figure 17.15a and b), which indicates thepresenceofthe
plasticizer bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in the investigated material. The detailed
thermal decomposition of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate was presented in earlier
publications of the author (P. K.) [2,4].
The presence of the plasticizer in one of the batch was the cause of the different
properties of the varnishes.