Page 465 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 465
3 Results 463
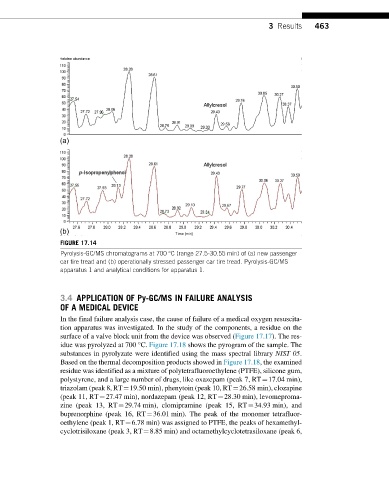
FIGURE 17.14
Pyrolysis-GC/MS chromatograms at 700 °C (range 27.5-30.55 min) of (a) new passenger
car tire tread and (b) operationally stressed passenger car tire tread. Pyrolysis-GC/MS
apparatus 1 and analytical conditions for apparatus 1.
3.4 APPLICATION OF Py-GC/MS IN FAILURE ANALYSIS
OF A MEDICAL DEVICE
In the final failure analysis case, the cause of failure of a medical oxygen resuscita-
tion apparatus was investigated. In the study of the components, a residue on the
surface of a valve block unit from the device was observed (Figure 17.17). The res-
idue was pyrolyzed at 700 °C. Figure 17.18 shows the pyrogram of the sample. The
substances in pyrolyzate were identified using the mass spectral library NIST 05.
Based on the thermal decomposition products showed in Figure 17.18, the examined
residue was identified as a mixture of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), silicone gum,
polystyrene, and a large number of drugs, like oxazepam (peak 7, RT¼17.04 min),
triazolam (peak 8, RT¼19.50 min), phenytoin (peak 10, RT¼26.58 min), clozapine
(peak 11, RT¼27.47 min), nordazepam (peak 12, RT¼28.30 min), levomeproma-
zine (peak 13, RT¼29.74 min), clomipramine (peak 15, RT¼34.93 min), and
buprenorphine (peak 16, RT¼36.01 min). The peak of the monomer tetrafluor-
oethylene (peak 1, RT¼6.78 min) was assigned to PTFE, the peaks of hexamethyl-
cyclotrisiloxane (peak 3, RT¼8.85 min) and octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (peak 6,