Page 66 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 66
60 CHAPTER 3 Boiler tube failures: Some case studies
Table 3.4 Observed ID Scale Thickness and Mean Tube Metal Temperature
of the Failed Platen Superheater Tube
Location of Scale Maximum Measured Estimated Mean
Thickness ID Scale Thickness Tube Metal
Measurement (mm) Temperature (°C) Figure No.
(a) Adjacent to 0.60 603 3.12
rupture of the
failed tube
(b) Diametrically 0.50 594 3.13
opposite to
rupture
(c) Away from 0.50 594 3.14
rupture
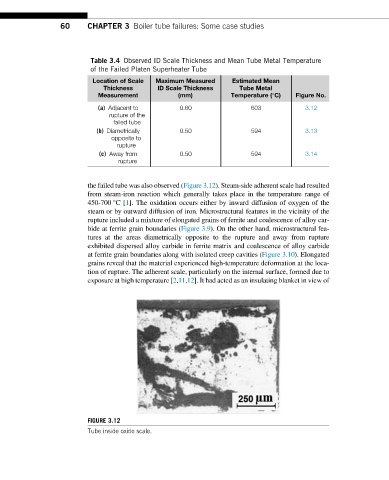
the failed tube was also observed (Figure 3.12). Steam-side adherent scale had resulted
from steam-iron reaction which generally takes place in the temperature range of
450-700 °C[1]. The oxidation occurs either by inward diffusion of oxygen of the
steam or by outward diffusion of iron. Microstructural features in the vicinity of the
rupture included a mixture of elongated grains of ferrite and coalescence of alloy car-
bide at ferrite grain boundaries (Figure 3.9). On the other hand, microstructural fea-
tures at the areas diametrically opposite to the rupture and away from rupture
exhibited dispersed alloy carbide in ferrite matrix and coalescence of alloy carbide
at ferrite grain boundaries along with isolated creep cavities (Figure 3.10). Elongated
grains reveal that the material experienced high-temperature deformation at the loca-
tion of rupture. The adherent scale, particularly on the internal surface, formed due to
exposure at high temperature [2,11,12]. It had acted as an insulating blanket in view of
FIGURE 3.12
Tube inside oxide scale.