Page 67 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 67
2 Case Studies 61
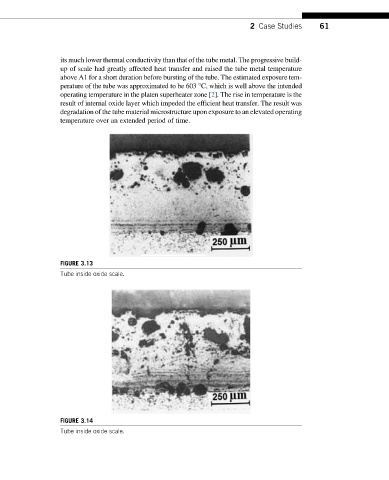
its much lower thermal conductivity than that of the tube metal. The progressive build-
up of scale had greatly affected heat transfer and raised the tube metal temperature
above A1 for a short duration before bursting of the tube. The estimated exposure tem-
perature of the tube was approximated to be 603 °C, which is well above the intended
operating temperature in the platen superheater zone [2]. The rise in temperature is the
result of internal oxide layer which impeded the efficient heat transfer. The result was
degradation of the tube material microstructure upon exposure to an elevated operating
temperature over an extended period of time.
FIGURE 3.13
Tube inside oxide scale.
FIGURE 3.14
Tube inside oxide scale.