Page 83 - Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing Principles and Practices
P. 83
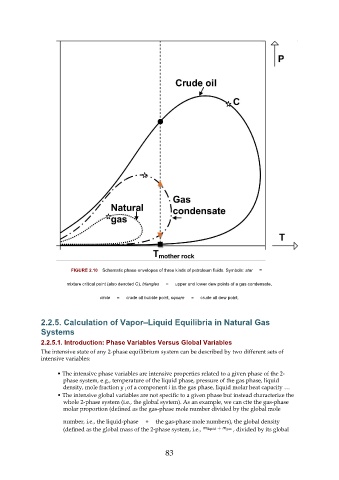
FIGURE 2.10 Schematic phase envelopes of three kinds of petroleum fluids. Symbols: star =
mixture critical point (also denoted C), triangles = upper and lower dew points of a gas condensate,
circle = crude oil bubble point, square = crude oil dew point.
2.2.5. Calculation of Vapor–Liquid Equilibria in Natural Gas
Systems
2.2.5.1. Introduction: Phase Variables Versus Global Variables
The intensive state of any 2-phase equilibrium system can be described by two different sets of
intensive variables:
• The intensive phase variables are intensive properties related to a given phase of the 2-
phase system, e.g., temperature of the liquid phase, pressure of the gas phase, liquid
density, mole fraction y of a component i in the gas phase, liquid molar heat capacity …
i
• The intensive global variables are not specific to a given phase but instead characterize the
whole 2-phase system (i.e., the global system). As an example, we can cite the gas-phase
molar proportion (defined as the gas-phase mole number divided by the global mole
number, i.e., the liquid-phase + the gas-phase mole numbers), the global density
(defined as the global mass of the 2-phase system, i.e., , divided by its global
83