Page 188 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 188
THERMOSETS
3.58 CHAPTER 3
with T = 340°C, excellent hot/wet properties at 274°C, and useful service temperature of
g
260°C or above.
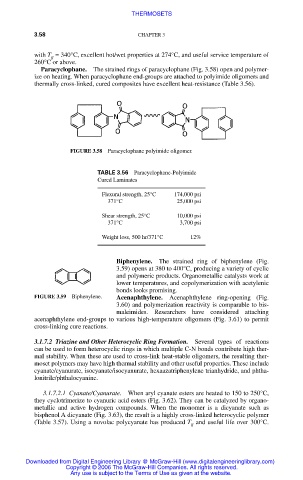
Paracyclophane. The strained rings of paracyclophane (Fig. 3.58) open and polymer-
ize on heating. When paracyclophane end-groups are attached to polyimide oligomers and
thermally cross-linked, cured composites have excellent heat-resistance (Table 3.56).
FIGURE 3.58 Paracyclophane polyimide oligomer.
TABLE 3.56 Paracyclophane-Polyimide
Cured Laminates
Flexural strength, 25°C 174,000 psi
371°C 25,000 psi
Shear strength, 25°C 10,000 psi
371°C 3,700 psi
Weight loss, 500 hr/371°C 12%
Biphenylene. The strained ring of biphenylene (Fig.
3.59) opens at 380 to 400°C, producing a variety of cyclic
and polymeric products. Organometallic catalysts work at
lower temperatures, and copolymerization with acetylenic
bonds looks promising.
FIGURE 3.59 Biphenylene. Acenaphthylene. Acenaphthylene ring-opening (Fig.
3.60) and polymerization reactivity is comparable to bis-
maleimides. Researchers have considered attaching
acenaphthylene end-groups to various high-temperature oligomers (Fig. 3.61) to permit
cross-linking cure reactions.
3.1.7.2 Triazine and Other Heterocyclic Ring Formation. Several types of reactions
can be used to form heterocyclic rings in which multiple C-N bonds contribute high ther-
mal stability. When these are used to cross-link heat-stable oligomers, the resulting ther-
moset polymers may have high thermal stability and other useful properties. These include
cyanate/cyanurate, isocyanate/isocyanurate, hexaazatriphenylene trianhydride, and phtha-
lonitrile/phthalocyanine.
3.1.7.2.1 Cyanate/Cyanurate. When aryl cyanate esters are heated to 150 to 250°C,
they cyclotrimerize to cyanuric acid esters (Fig. 3.62). They can be catalyzed by organo-
metallic and active hydrogen compounds. When the monomer is a dicyanate such as
bisphenol A dicyanate (Fig. 3.63), the result is a highly cross-linked heterocyclic polymer
(Table 3.57). Using a novolac polycyanate has produced T and useful life over 300°C.
g
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.