Page 186 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 186
THERMOSETS
3.56 CHAPTER 3
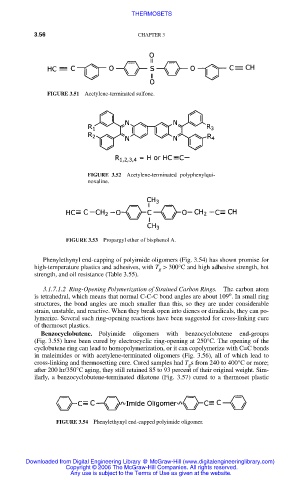
FIGURE 3.51 Acetylene-terminated sulfone.
FIGURE 3.52 Acetylene-terminated polyphenylqui-
noxaline.
FIGURE 3.53 Propargyl ether of bisphenol A.
Phenylethynyl end-capping of polyimide oligomers (Fig. 3.54) has shown promise for
high-temperature plastics and adhesives, with T > 300°C and high adhesive strength, hot
g
strength, and oil resistance (Table 3.55).
3.1.7.1.2 Ring-Opening Polymerization of Strained Carbon Rings. The carbon atom
o
is tetrahedral, which means that normal C-C-C bond angles are about 109 . In small ring
structures, the bond angles are much smaller than this, so they are under considerable
strain, unstable, and reactive. When they break open into dienes or diradicals, they can po-
lymerize. Several such ring-opening reactions have been suggested for cross-linking cure
of thermoset plastics.
Benzocyclobutene. Polyimide oligomers with benzocyclobutene end-groups
(Fig. 3.55) have been cured by electrocyclic ring-opening at 250°C. The opening of the
cyclobutene ring can lead to homopolymerization, or it can copolymerize with C=C bonds
in maleimides or with acetylene-terminated oligomers (Fig. 3.56), all of which lead to
cross-linking and thermosetting cure. Cured samples had T s from 240 to 400°C or more;
g
after 200 hr/350°C aging, they still retained 85 to 93 percent of their original weight. Sim-
ilarly, a benzocyclobutene-terminated diketone (Fig. 3.57) cured to a thermoset plastic
FIGURE 3.54 Phenylethynyl end-capped polyimide oligomer.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.