Page 182 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 182
THERMOSETS
3.52 CHAPTER 3
TABLE 3.51 Bis-Maleimide Cured Properties
Flexural modulus, 25°C 4000 kpsi
250°C 3200 kpsi
Aged 3000 hr/250°C 2600 kpsi
Flexural strength, 25°C 70 kpsi
250°C 50 kpsi
Aged 3000 hr/250°C 26 kpsi
Tensile strength 50 kpsi
Compressive strength 50 kpsi
Notched impact strength 13 kpsi
T g 296°C
14
Volume resistivity 6 × 10 Ω-cm
Dielectric constant 4.5
Dissipation factor 0.012
Dielectric strength 25 kV/mm
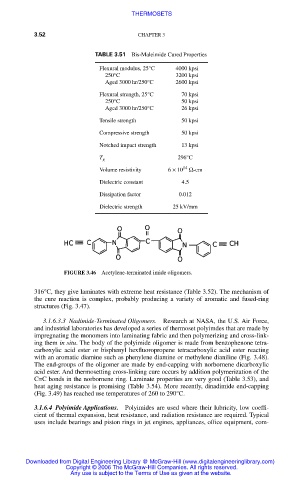
FIGURE 3.46 Acetylene-terminated imide oligomers.
316°C, they give laminates with extreme heat resistance (Table 3.52). The mechanism of
the cure reaction is complex, probably producing a variety of aromatic and fused-ring
structures (Fig. 3.47).
3.1.6.3.3 Nadimide-Terminated Oligomers. Research at NASA, the U.S. Air Force,
and industrial laboratories has developed a series of thermoset polyimdes that are made by
impregnating the monomers into laminating fabric and then polymerizing and cross-link-
ing them in situ. The body of the polyimide oligomer is made from benzophenone tetra-
carboxylic acid ester or bisphenyl hexfluoropropene tetracarboxylic acid ester reacting
with an aromatic diamine such as phenylene diamine or methylene dianiline (Fig. 3.48).
The end-groups of the oligomer are made by end-capping with norbornene dicarboxylic
acid ester. And thermosetting cross-linking cure occurs by addition polymerization of the
C=C bonds in the norbornene ring. Laminate properties are very good (Table 3.53), and
heat aging resistance is promising (Table 3.54). More recently, dinadimide end-capping
(Fig. 3.49) has reached use temperatures of 260 to 290°C.
3.1.6.4 Polyimide Applications. Polyimides are used where their lubricity, low coeffi-
cient of thermal expansion, heat resistance, and radiation resistance are required. Typical
uses include bearings and piston rings in jet engines, appliances, office equipment, com-
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.