Page 235 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 235
ELASTOMERS
ELASTOMERS 4.27
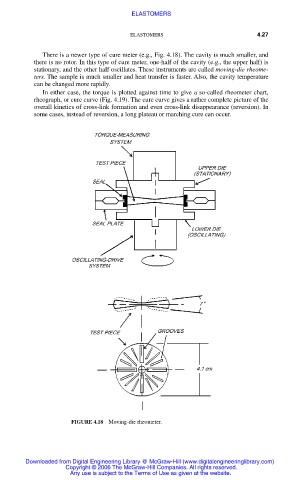
There is a newer type of cure meter (e.g., Fig. 4.18). The cavity is much smaller, and
there is no rotor. In this type of cure meter, one-half of the cavity (e.g., the upper half) is
stationary, and the other half oscillates. These instruments are called moving-die rheome-
ters. The sample is much smaller and heat transfer is faster. Also, the cavity temperature
can be changed more rapidly.
In either case, the torque is plotted against time to give a so-called rheometer chart,
rheograph, or cure curve (Fig. 4.19). The cure curve gives a rather complete picture of the
overall kinetics of cross-link formation and even cross-link disappearance (reversion). In
some cases, instead of reversion, a long plateau or marching cure can occur.
FIGURE 4.18 Moving-die rheometer.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.