Page 234 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 234
ELASTOMERS
4.26 CHAPTER 4
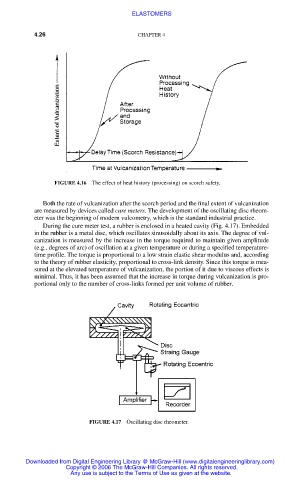
FIGURE 4.16 The effect of heat history (processing) on scorch safety.
Both the rate of vulcanization after the scorch period and the final extent of vulcanization
are measured by devices called cure meters. The development of the oscillating disc rheom-
eter was the beginning of modern vulcometry, which is the standard industrial practice.
During the cure meter test, a rubber is enclosed in a heated cavity (Fig. 4.17). Embedded
in the rubber is a metal disc, which oscillates sinusoidally about its axis. The degree of vul-
canization is measured by the increase in the torque required to maintain given amplitude
(e.g., degrees of arc) of oscillation at a given temperature or during a specified temperature-
time profile. The torque is proportional to a low strain elastic shear modulus and, according
to the theory of rubber elasticity, proportional to cross-link density. Since this torque is mea-
sured at the elevated temperature of vulcanization, the portion of it due to viscous effects is
minimal. Thus, it has been assumed that the increase in torque during vulcanization is pro-
portional only to the number of cross-links formed per unit volume of rubber.
FIGURE 4.17 Oscillating disc rheometer.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.