Page 251 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 251
ELASTOMERS
ELASTOMERS 4.43
SCHEME 12
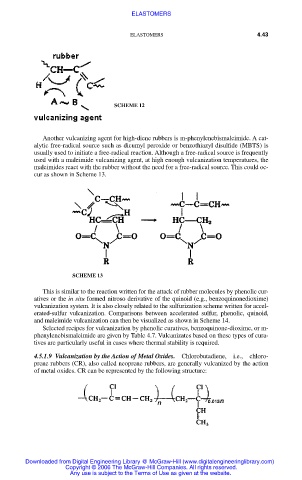
Another vulcanizing agent for high-diene rubbers is m-phenylenebismaleimide. A cat-
alytic free-radical source such as dicumyl peroxide or benzothiazyl disulfide (MBTS) is
usually used to initiate a free-radical reaction. Although a free-radical source is frequently
used with a maleimide vulcanizing agent, at high enough vulcanization temperatures, the
maleimides react with the rubber without the need for a free-radical source. This could oc-
cur as shown in Scheme 13.
SCHEME 13
This is similar to the reaction written for the attack of rubber molecules by phenolic cur-
atives or the in situ formed nitroso derivative of the quinoid (e.g., benzoquinonedioxime)
vulcanization system. It is also closely related to the sulfurization scheme written for accel-
erated-sulfur vulcanization. Comparisons between accelerated sulfur, phenolic, quinoid,
and maleimide vulcanization can then be visualized as shown in Scheme 14.
Selected recipes for vulcanization by phenolic curatives, benzoquinone-dioxime, or m-
phenylenebismaleimide are given by Table 4.7. Vulcanizates based on these types of cura-
tives are particularly useful in cases where thermal stability is required.
4.5.1.9 Vulcanization by the Action of Metal Oxides. Chlorobutadiene, i.e., chloro-
prene rubbers (CR), also called neoprene rubbers, are generally vulcanized by the action
of metal oxides. CR can be represented by the following structure:
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.