Page 255 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 255
ELASTOMERS
ELASTOMERS 4.47
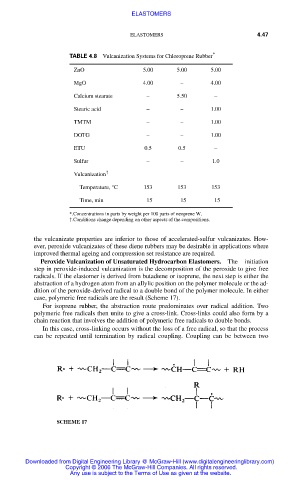
TABLE 4.8 Vulcanization Systems for Chloroprene Rubber *
ZnO 5.00 5.00 5.00
MgO 4.00 – 4.00
Calcium stearate – 5.50 –
Stearic acid – – 1.00
TMTM – – 1.00
DOTG – – 1.00
ETU 0.5 0.5 –
Sulfur – – 1.0
Vulcanization †
Temperature, °C 153 153 153
Time, min 15 15 15
*.Concentrations in parts by weight per 100 parts of neoprene W.
†.Conditions change depending on other aspects of the compositions.
the vulcanizate properties are inferior to those of accelerated-sulfur vulcanizates. How-
ever, peroxide vulcanizates of these diene rubbers may be desirable in applications where
improved thermal ageing and compression set resistance are required.
Peroxide Vulcanization of Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Elastomers. The initiation
step in peroxide-induced vulcanization is the decomposition of the peroxide to give free
radicals. If the elastomer is derived from butadiene or isoprene, the next step is either the
abstraction of a hydrogen atom from an allylic position on the polymer molecule or the ad-
dition of the peroxide-derived radical to a double bond of the polymer molecule. In either
case, polymeric free radicals are the result (Scheme 17).
For isoprene rubber, the abstraction route predominates over radical addition. Two
polymeric free radicals then unite to give a cross-link. Cross-links could also form by a
chain reaction that involves the addition of polymeric free radicals to double bonds.
In this case, cross-linking occurs without the loss of a free radical, so that the process
can be repeated until termination by radical coupling. Coupling can be between two
SCHEME 17
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.