Page 263 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 263
ELASTOMERS
ELASTOMERS 4.55
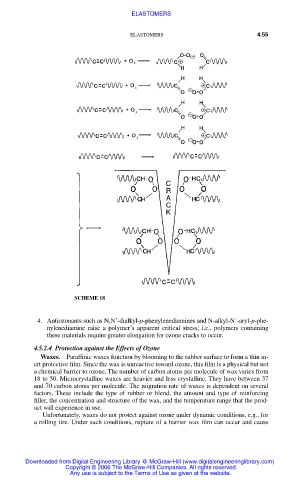
SCHEME 18
4. Antiozonants such as N,N´-dialkyl-p-phenylenediamines and N-alkyl-N´-aryl-p-phe-
nylenediamine raise a polymer’s apparent critical stress; i.e., polymers containing
these materials require greater elongation for ozone cracks to occur.
4.5.2.4 Protection against the Effects of Ozone
Waxes. Paraffinic waxes function by blooming to the rubber surface to form a thin in-
ert protective film. Since the wax is unreactive toward ozone, this film is a physical but not
a chemical barrier to ozone. The number of carbon atoms per molecule of wax varies from
18 to 50. Microcrystalline waxes are heavier and less crystalline. They have between 37
and 70 carbon atoms per molecule. The migration rate of waxes is dependent on several
factors. These include the type of rubber or blend, the amount and type of reinforcing
filler, the concentration and structure of the wax, and the temperature range that the prod-
uct will experience in use.
Unfortunately, waxes do not protect against ozone under dynamic conditions, e.g., for
a rolling tire. Under such conditions, rupture of a barrier wax film can occur and cause
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.